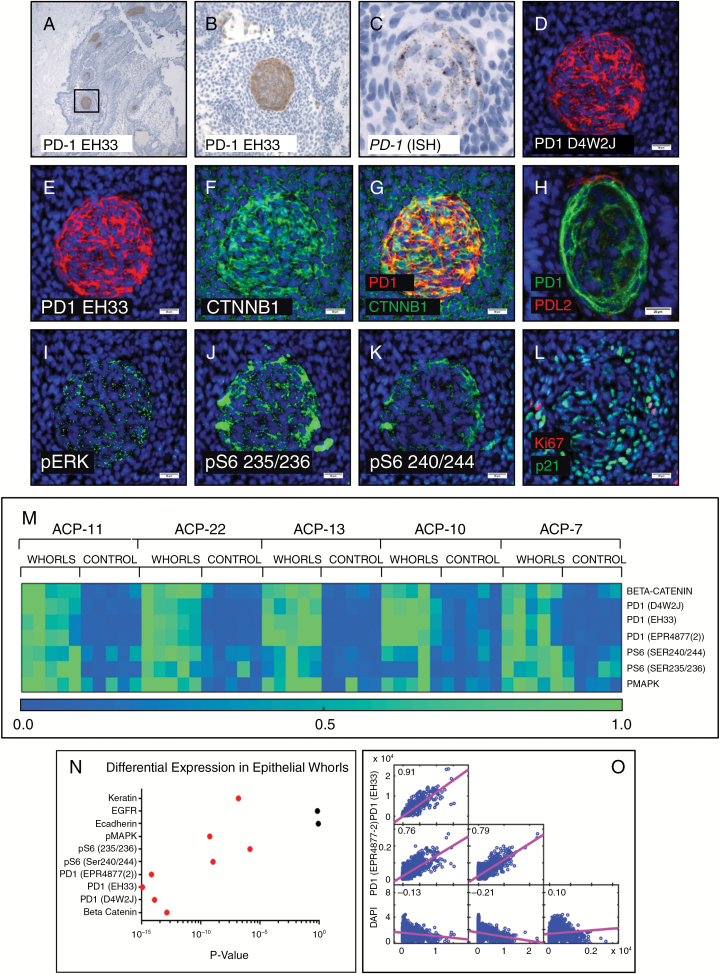
Fig. 3 .
PD-1 IHC in ACP showed tumor cell–intrinsic PD-1 expression in whorls of tumor epithelium (A, B). In situ hybridization showed expression of PD-1 mRNA in epithelial whorls (C). Multiplexed cyclic immunofluorescence (t-CyCIF) showed co-localization of PD-1 (D, E) using multiple antibodies, and nuclear beta-catenin (F, G) in the whorled cells. PD-L2 positive cells were observed closely associated with whorls (H) (different whorl pictured than D–L). Whorls showed elevated phospho-p44/42 MAPK (Erk1/2) (Thr202/Tyr204) (I), phospho-S6 (Ser235/236) (J), and (Ser240/244) (K). PD-1 expressing whorls had diffuse nuclear p21Cip1/Waf1 but MIB-1/Ki-67 staining was not typically present (L). Quantitative analysis (heatmaps of 5 ACP resections depicted with 0.0 [low] to 1.0 [high] expression by normalized mean intensity) (M) showed significantly increased expression (P < 0.025, red dots indicate significance) (N) of PD-1, pS6, and pERK in whorls compared with adjacent non-whorled epithelium. Multiple PD-1 antibodies showed high pixel-by-pixel correlation coefficients (O). Scale bar 100 µm (C); scale bars 20 µm (D–L).