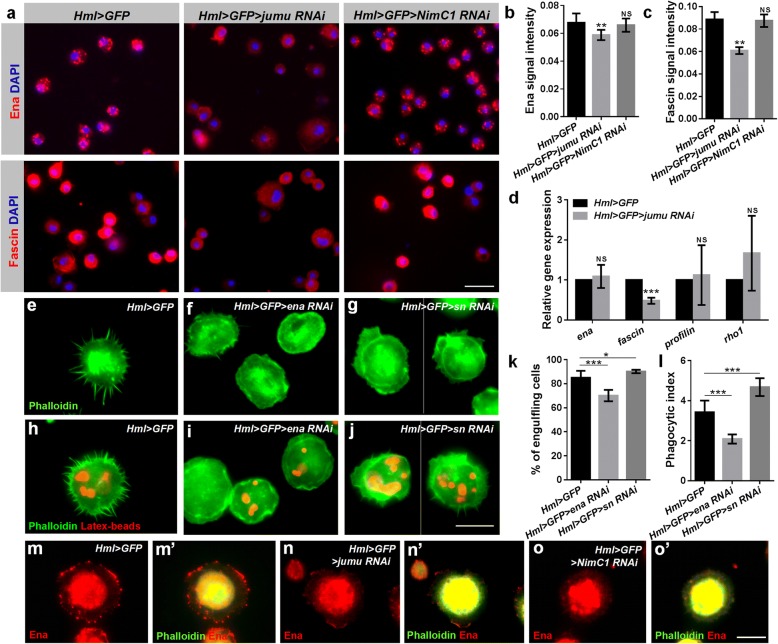
Fig. 4.
Expression levels of proteins associated with actin filopodium formation are changed in jumu knockdown hemocytes. a Immunostaining against Ena (red) and Fascin (red) shows that the expression of Ena and Fascin is reduced in jumu knockdown hemocytes compared with the expression in the controls; however, the knockdown of NimC1 does not affect the expression of Ena and Fascin. b, c Quantification of signal intensities. d Real-time PCR analysis of ena, fascin, profilin and rho1 levels in jumu knockdown hemocytes. e-g Phalloidin staining (green) shows that the number and length of filopodia are reduced in the circulating hemocytes of Hml > GFP > ena RNAi and Hml > GFP > sn RNAi. h-j Circulating hemocytes of Hml > GFP > ena RNAi and Hml > GFP > sn RNAi isolated from third-instar larvae injected with latex beads (red) 1 h postinjection show defects in filopodia (green). k, l Quantification of the percentage of engulfing cells and phagocytic indexes based on phagocytosis assays. m-o’ Immunostaining against Ena (red) and phalloidin staining (green) shows that Ena is enriched at the tips of filopodia and lamellipodia in control circulating hemocytes; however, the expression level of Ena is markedly reduced at the tips of filopodia and lamellipodia in Hml > GFP > jumu RNAi (n and n’) and Hml > GFP > NimC1 RNAi (o and o’) circulating hemocytes. Error bars represent the S.E.M of at least 3 independent experiments; NS, not significant; *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001 (Student’s t-test). Scale bars: 20 μm (a); 10 μm (e-j, m-o’)