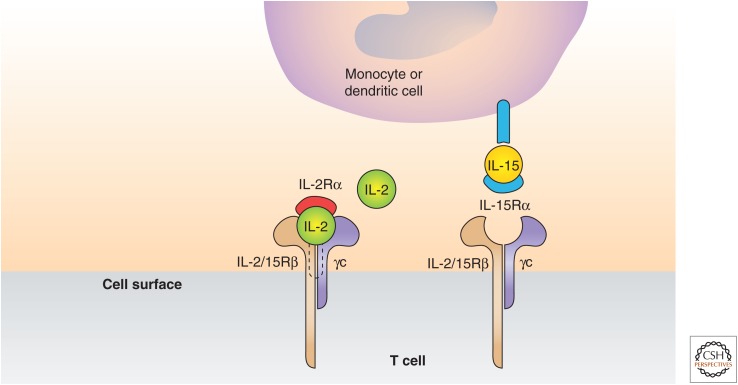
Figure 2.
Model of interaction of interleukin (IL)-2 and IL-15 with their receptors. IL-2 is predominantly a secreted cytokine that binds to preformed high-affinity heterotrimeric receptors. In contrast, IL-15 is a membrane-associated molecule that signals as part of an immunological synapse between antigen-presenting cells and natural killer (NK) cells, γΔ, and CD8 T cells. IL-15Rα on the surface of activated monocytes or dendritic cells (DCs) presents IL-15 in trans to cells that express IL-2/IL-15Rβ and γ chain (γc), thereby allowing signaling through these complexes. (Based on figures in Waldmann 2006.)