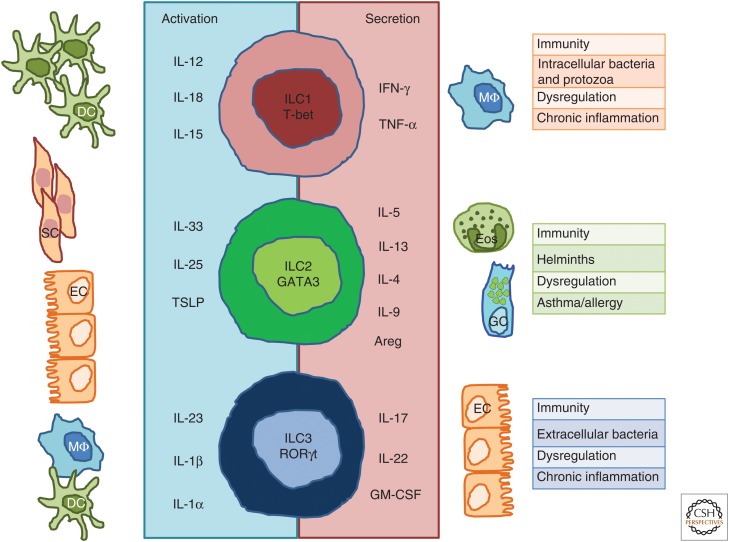
Figure 2.
Innate lymphoid cell (ILC) subsets and cytokines. ILC1s depend on transcription factor T-bet for their function and produce interferon (IFN)-γ and tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α in response to interleukin (IL)-12, IL-15, and IL-18 derived from dendritic cells (DCs). ILC2s require GATA3 and are endowed with the ability to secrete IL-4, IL-5, IL-9, IL-13, and amphiregulin (Areg) in response to IL-25, IL-33, and thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP) derived from epithelial cells and tissue-resident immune cells. ILC3s depend on the transcription factor RAR-related orphan receptor γt (RORγt) and secrete IL-17, IL-22, and granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) in response to IL-23, IL-1β, and IL-1α derived from macrophages and DCs. ILC immune responses are shaped to cope with different types of pathogens, although their dysregulation might lead to chronic inflammation. SC, Stromal cell; EC, epithelial cell; Eos, eosinophils; GC, goblet cell.