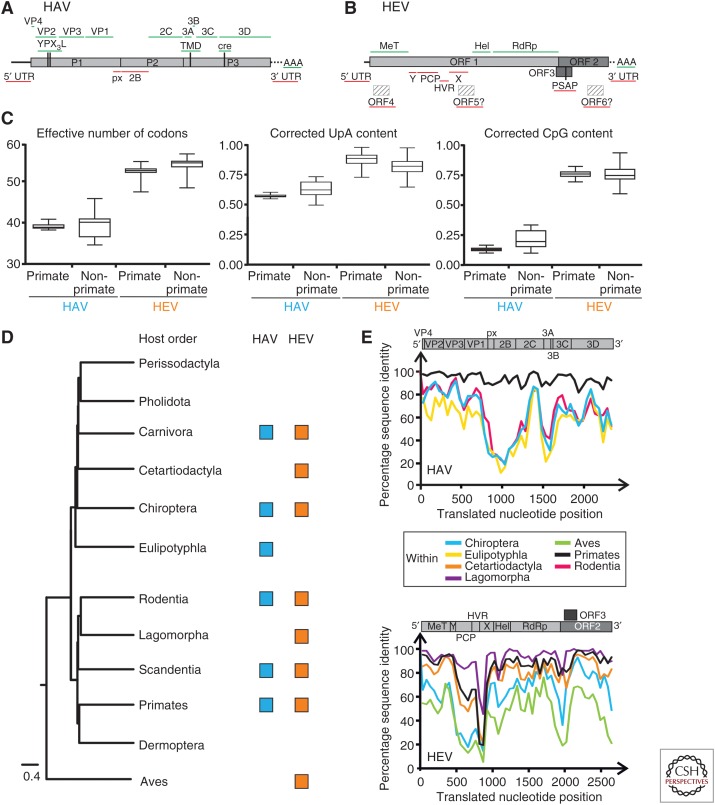
Figure 2.
Genomic variability among hepatoviruses and hepeviruses. Genome organization showing conservation of putative functional domains within (A) hepatoviruses, and (B) hepeviruses. Conserved domains (green) are depicted above, and nonconserved domains (red) are depicted below graphs. (C) Relative CpG, UpA dinucleotide content and effective number of codons in hepatoviruses and hepeviruses calculated using SSE 1.3 software (Simmonds 2012). Median (bar) and quartiles (box and whiskers) are shown. (D) Phylogenetic relationships of boreoeutherian vertebrate orders, including an avian outgroup. (Phlyogeny adapted from Foley et al. 2016.) Squares indicate vertebrate orders in which hepatoviruses or orthohepeviruses were found. (E) Amino acid sequence identities within hepatoviruses (top) and hepeviruses (bottom) of different host orders. Generally, representative viruses from each host order were tagged and sequence identities within families were plotted using a fragment length of 400 and a step size of 200 amino acid residues. Alignment gaps were excluded from the analysis. A schematic representation of the hepatitis A virus (HAV)/hepatitis E virus (HEV) genome organization is depicted at the top for orientation. For HAV, complete coding sequences of the polyproteins were translationally aligned. Accession numbers of representative sequences were, within Primates: AB020564, AY644676, AB279732, D00924; Chiroptera: KT452742, KT452730, KT452729, KT452714; Rodentia: KT452735, KT452685, KT229611, KT452644, KT452637; Eulipotyphla: KT452691, KT452658. For HEV, the complete open reading frame (ORF)1 and ORF2 were concatenated and translationally aligned. ORF3 is only shown for indication of its position. Accession numbers of representative sequences were, within Lagomorpha: FJ906895, KJ013415; Primates: M73218, M74506, AP003430, AB197673; Cetartiodactyla: AF082843, AB189071, AB573435, AB602441, KF951328, KJ496143, KX387865; Chiroptera: JQ001749, KJ562187, KX513953; Aves: KX589065, KU670940, AY535004. Hel, Helicase; HVR, hypervariable region; MT, methyltransferase; PCP, papain-like cysteine protease; RdRp, RNA-dependent RNA polymerase; TMD, transmembrane domain; UTR, untranslated region; X, X domain/ADP-ribose-binding module; Y, Y-like domain.