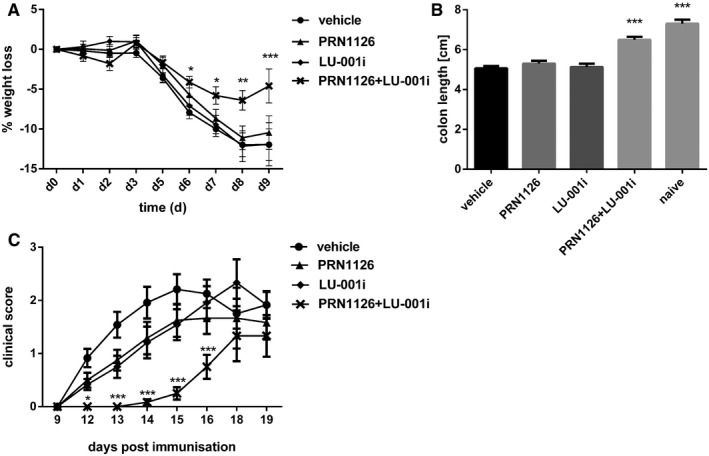
Figure 6. The amelioration of DSS‐induced colitis and EAE relies on the joint inhibition of LMP7 and LMP2.
-
A, BColitis was induced by oral administration of 3% DSS. Mice were treated daily (s.c.) with LU‐001i (15 mg/kg), PRN1126 (40 mg/kg), PRN1126 + LU‐001i (40 + 15 mg/kg), or vehicle starting from the begin of the experiment. Data points represent means ± s.e.m. of 15 mice pooled from three independent experiments. (A) The body weight of individual mice was monitored daily, and the percent weight loss (y‐axis) was plotted versus time (x‐axis). All data were statistically compared to the vehicle‐treated group. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. Two‐way ANOVA. (B) On day 9 after initiation of DSS treatment, colon lengths were measured (n = 15). Naïve mice (n = 5) were used as healthy controls. All data were statistically compared to the vehicle‐treated group. ***P < 0.001. One‐way ANOVA.
-
CMice were immunized with MOG35–55 peptide and were monitored daily for clinical symptoms of EAE. Mice were treated intermittently with three times a week (s.c.) schedule with LU‐001i (15 mg/kg), PRN1126 (40 mg/kg), PRN1126 + LU‐001i (40 + 15 mg/kg), or vehicle starting from the beginning of the experiment. Data points represent the means of the clinical scores ± s.e.m. of 12 mice pooled from two independent experiments. All data were statistically compared to the vehicle‐treated group. *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001. Two‐way ANOVA.
