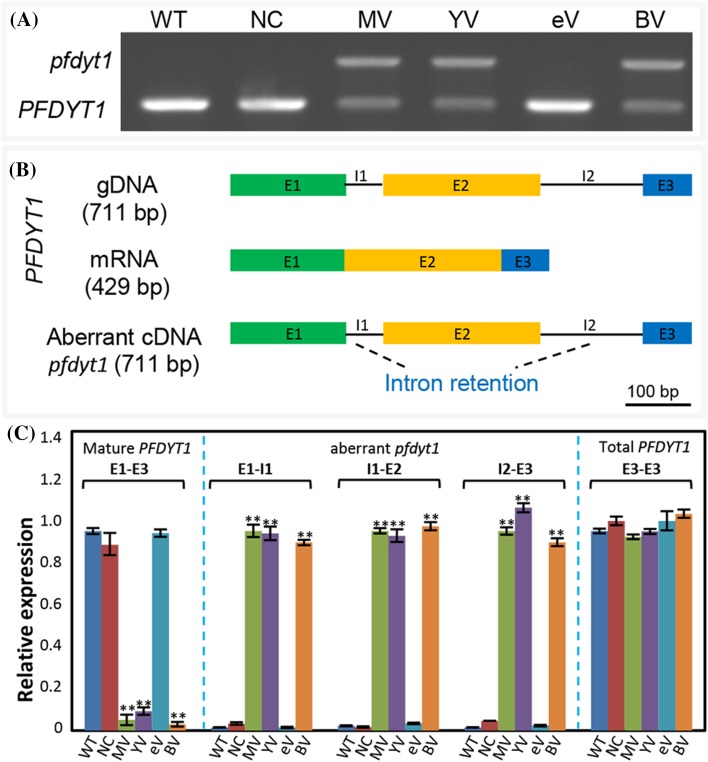
Fig. 7.
Accumulation of aberrant pfdyt1 transcripts in EJC core knockdowns. a Full-length transcripts of PFDYT1 in floral buds revealed by RT-PCR. WT, NC, MV, YV, eV and BV respectively represent wild type, negative control (TRV2), PFMAGO-, PFY14-, PFeIF4AIII- and PFBTZ-VIGS plants. The extension time was 30 s. A larger transcript designated pfdyt1 occurred in the indicated flowers. b The PFDYT1 splicing is altered in the knockdowns of the EJC core genes. The structure of gDNA, cDNA in WT plants, and aberrant transcript in the VIGS plants was demonstrated. Color rectangles, exons (E1–E3); black lines, introns (I1, I2). c Relative expression levels of mature PFDYT1, abnormal pfdyt1 (E1–I1, I1–E2, I2–E3) and total (E3–E3) mRNA as indicated. Total RNAs from floral buds (7DBF) of WT, NC and PFMAGO-, PFY14-, PfeIF4AIII- and PFBTZ-VIGS plants were subjected to qRT-PCR. PFACTIN mRNAs were used as internal control. The extension time was 10 s. In detection of mature PFDYT1 RNA (left), the expression in WT was set as 1, while in detection of aberrant pfdyt1 transcripts (right), the expression in floral buds of each MV was set as 1. Three independent biological samples were used, and error bars represent SD. Significance relative to WT was evaluated by a two-tailed student’s t test, and double asterisks indicates significance at P < 0.01