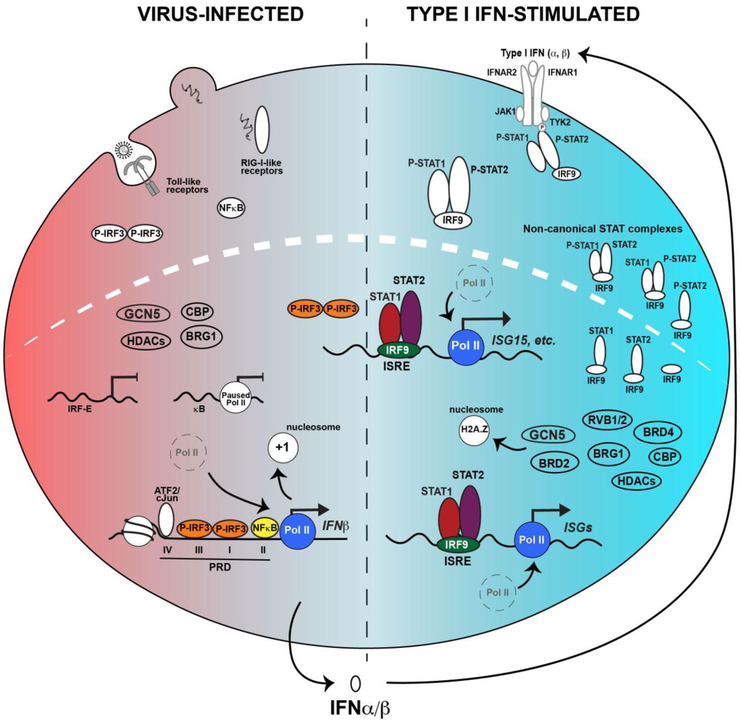
Figure 3. IRFs and STATs drive the IFN antiviral response.
Depiction of the two-phase antiviral response following virus infection (left), leading to IFN-mediated JAK-STAT signaling (right). The networks of both primary response genes activated by IRF3 and NFκB and IFN target genes activated by ISGF3, combine to produce a potent and coordinated response to infection. The ability of IRF proteins to recognize common core response elements leads to overlapping patterns of target gene expression, as exemplified by genes like ISG15 that are activated by IRF3 during virus infection and ISGF3 following IFN stimulation. In addition to the canonical IRF and ISGF3 factors, non-canonical STAT complexes are present both prior to and following IFN stimulation.