Figure 8.
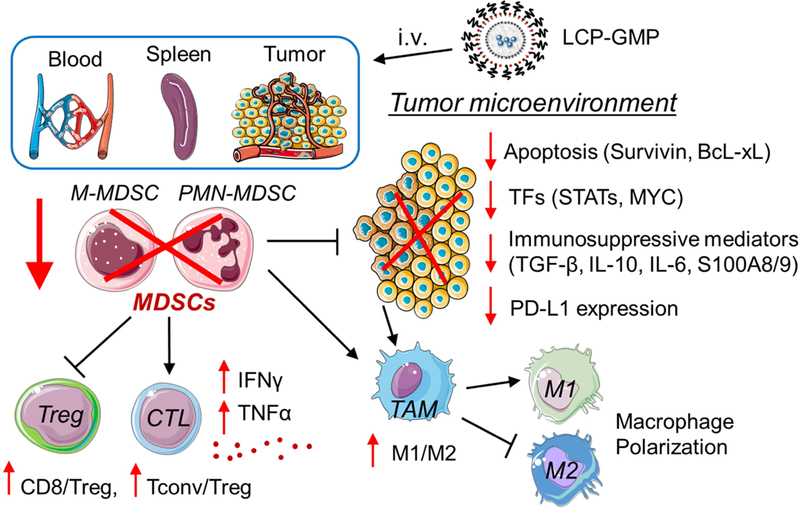
Schematic illustration of LCP-GMP-mediated immunomodulation. After intravenous (i.v.) injections, LCP-GMP triggered significant apoptosis; largely depleted immunosuppressive MDSCs in the peripheral blood, spleen and tumor; downregulated the expressions of pro-tumor transcription factors (TFs), immunosuppressive mediators and checkpoint protein PD-L1 in tumors; induced the polarization of tumor-associated macrophages (TAM) from the pro-tumor M2 phenotype to antitumor M1 phenotype; selectively depleted immunosuppressive Tregs without compromising other tumor-infiltrating T cells; enhanced the production of proinflammatory cytokines in CD8+ T cells and inhibited tumor progression.
