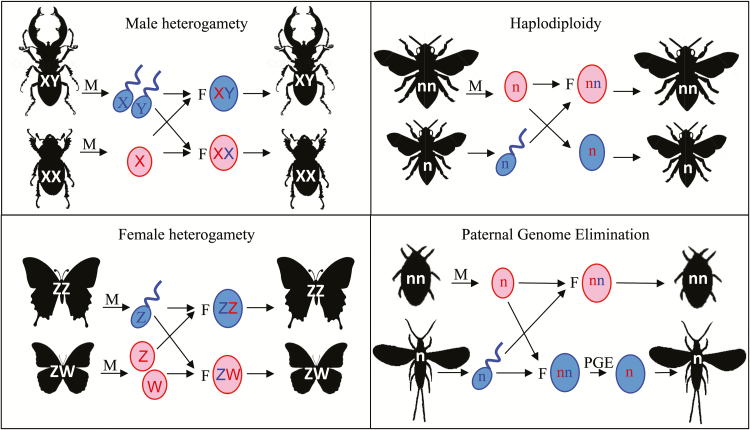
Figure 1.
Common sex determination systems in insects. With male heterogamety, males have heteromorphic sex chromosomes (XY), and females are homomorphic (XX). With female heterogamety, females have heteromorphic sex chromosomes (ZW), and males are homomorphic (ZZ). Under haplodiploid sex determination, females develop from diploid fertilized eggs (nn), and males develop from unfertilized haploid eggs (n). Under PGE, males develop from initially fertilized eggs, but eliminate their paternal genome during development (and become functionally haploid). Sperm are shown in blue, and eggs are shown in red. M indicates meiosis, F indicates fertilization, and PGE the elimination of the paternal genome.