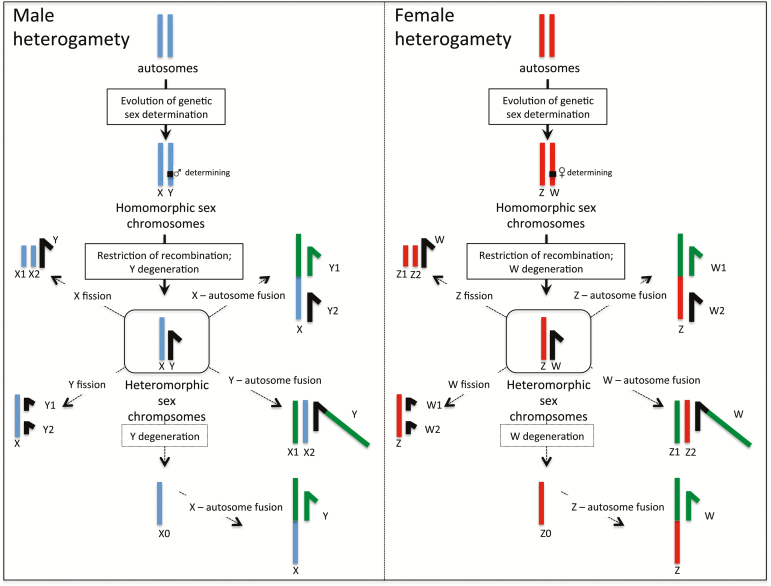
Figure 2.
Sex chromosome differentiation and origination of complex sex chromosomes. Sex chromosomes evolve from ordinary autosomes, after the emergence of a sex-determining locus. A restriction of recombination allows for differentiation, and Y/W chromosomes degenerate by an accumulation of deleterious mutations, and may be entirely lost (XO or ZO systems). Both fusions and fissions between sex chromosomes and autosomes can lead to the evolution of complex sex chromosomes (such as X1X2Y and XY1Y2 or Z1Z2W and ZW1W2 systems). Note that fusions are associated with a decrease in total chromosome number, while fissions increase the chromosome count.