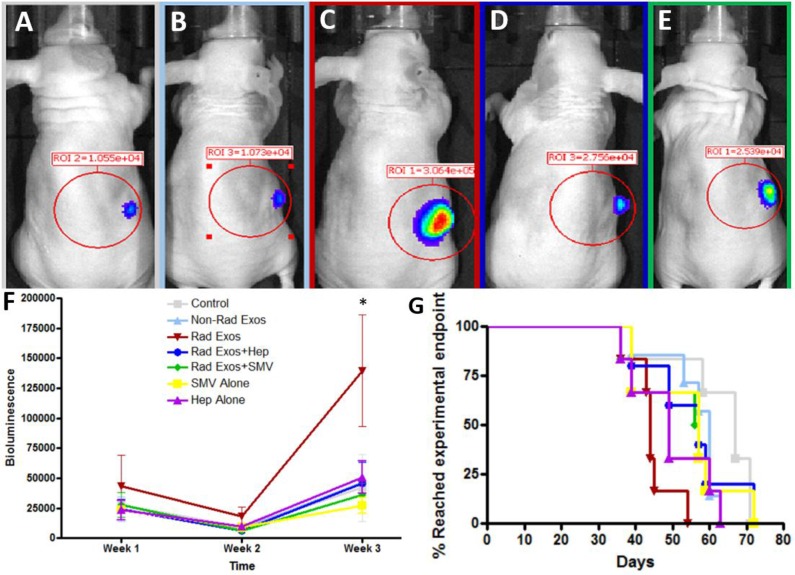
Figure 4. In vivo analysis of radiation derived exosome effect and therapeutic blockade.
Representative IVIS images of (A) Control (B) Non-radiation exosomes (C) Radiation-derived exosomes, (D) Radiation-derived exosomes plus daily heparin (Hep), (E) Radiation-derived exosomes plus daily simvastatin (SMV) treatment. Mice treated with radiation-derived exosomes had visually larger tumors when compared to control. When co-treating mice with radiation-derived exosomes plus heparin or simvastatin, the tumor size decreased and was comparable to control levels. (F) Tumor progression over time was quantified with IVIS counts. Mice treated with radiation-derived exosomes (represented as “Rad Exos”) had an increase in tumor progression and when co-treating with Hep or SMV tumor progression was similar to baseline (p<0.05). (G) Mice treated with radiation-derived exosomes had a decrease in survival time but when co-treating with heparin or simvastatin the mouse survival increased.