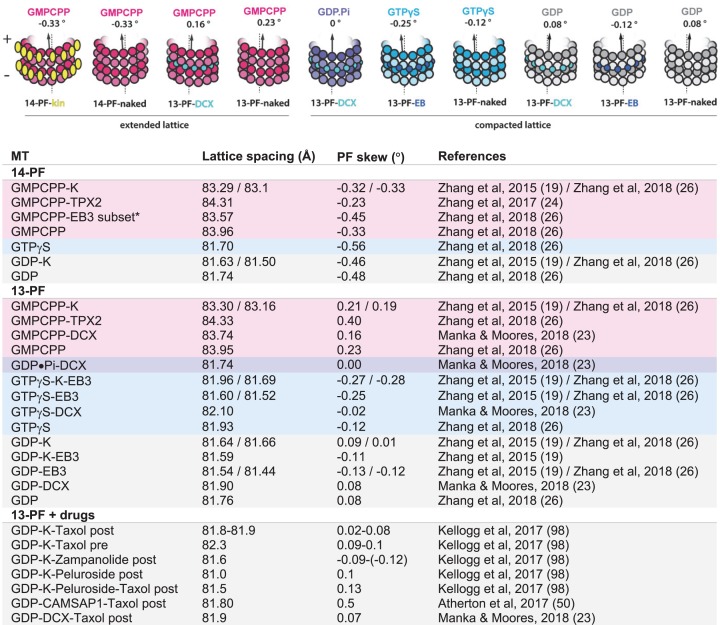
Figure 3. Modulation of MT-lattice conformation by MT-binding proteins and drugs.
Top, schematic representation of various MT lattices used in studies addressing the mechanism of dynamic instability. Bottom, table summarizing influence of PF-number, nucleotide state (color-coded along the rows) and MT-binding proteins and drugs on major MT lattice parameters: the axial repeat distance of tubulin dimers (lattice spacing) and PF skew. *EB3 induces hydrolysis of GMPCPP leading to compaction of MT lattice—only a small subset of GMPCPP-EB3 MTs has been shown to exhibit the extended lattice conformation. The impact of different drugs on MT structure depends on whether they are present during MT assembly (pre) or are added after the assembly (post). The summary is limited to mammalian tubulin due to the lack of unambiguous characterization of these parameters in yeast [80–82] and other organisms; K, kinesin-1 motor domain.