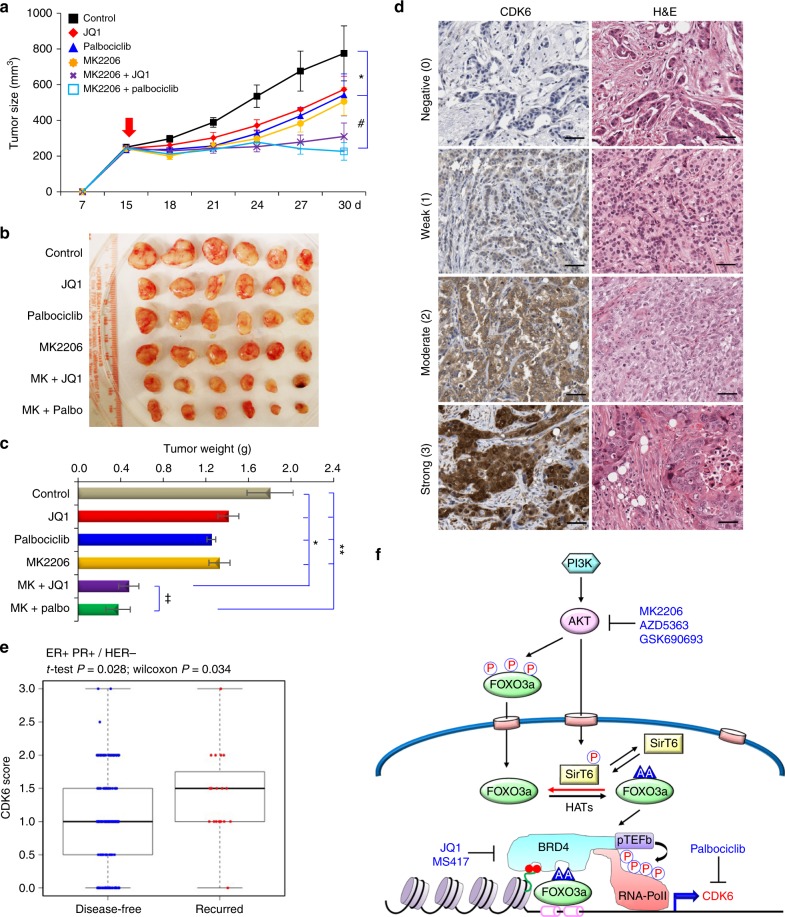
Fig. 8.
The FOXO3a-BRD4-CDK6 axis is critical for AKTi resistance in vivo. a, b BT474 cells were injected into athymic mice subcutaneously. When tumors from mice reached 250 mm3, mice were divided into six groups (six mice/group) and treated with solvent control, MK2206 (90 mg/kg), JQ1 (50 mg/kg), Palbociclib (100 mg/kg), or in combinations, respectively. The size of tumor was recorded every 3 days. Data are represented as a mean ± SEM from six mice. */#p < 0.01 when combinatory treatment group is compared with either control or single-agent treatment group. c Tumor weight was also measured from above. Data are represented as a mean ± SEM from six mice. Data are represented as a mean ± SEM from six mice. */⁑p < 0.01 when combinatory treatment group is compared with either control or single-agent treatment group. ‡p > 0.05 when both combinatory treatment groups were compared. d, e The 343 surgical specimens of breast cancer were immuno-stained using antibody against CDK6 and the control serum (data not shown). Images with consecutive IHC staining of CDK6 and H&E staining in four cases of breast tumors are shown (Scale bar = 100 μm). Recurrence rate was calculated according to CDK6 scores and clinical information of these patients. f A proposed model illustrating the formation of FOXO3a-BRD4 complex at the enhancer/promoter of CDK6, which leads to the transcriptional activation of CDK6 gene in response to AKTi. Either targeting FOXO3a-BRD4 complex by BET inhibitors or inhibition of CDK6 by Palbociclib reverses the AKTi resistance