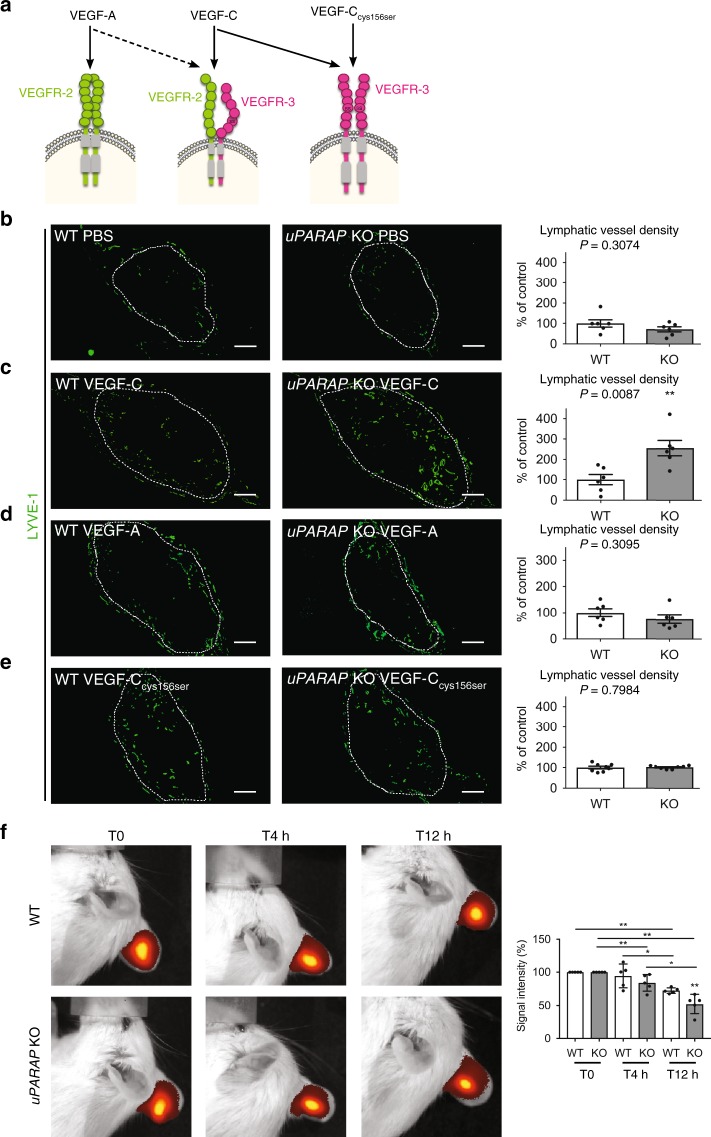
Fig. 2.
uPARAP deficiency stimulates VEGF-C-driven lymphangiogenesis. a Schematic of VEGF ligand interaction with VEGFR-2 and VEGFR-3 homodimers or VEGFR-2/VEGFR-3 heterodimers. b–e Gelatin sponges soaked with PBS (b), VEGF-C (c), VEGF-A (d), or mutated VEGF-CCys156Ser (e) were implanted in mouse ears. White dots delineate the sponge in the ear. Lymphatic vasculature was examined by LYVE-1 (green) immunostaining. Histograms represent the area density of vessels quantified by a computer-assisted method and expressed as percentage of WT control (b–d n = 6; e n = 8). Bars = 500 µm. f Indocyanin Green (ICG) clearance in VEGF-C-soaked sponges in uPARAP WT and KO mice using Xenogen IVIS. Histogram represents mean fluorescence signal detected at each time point (n = 5). All results are expressed as mean ± SEM, and statistical analyses were performed using a non-parametric Mann–Whitney test. *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01