Figure 3.
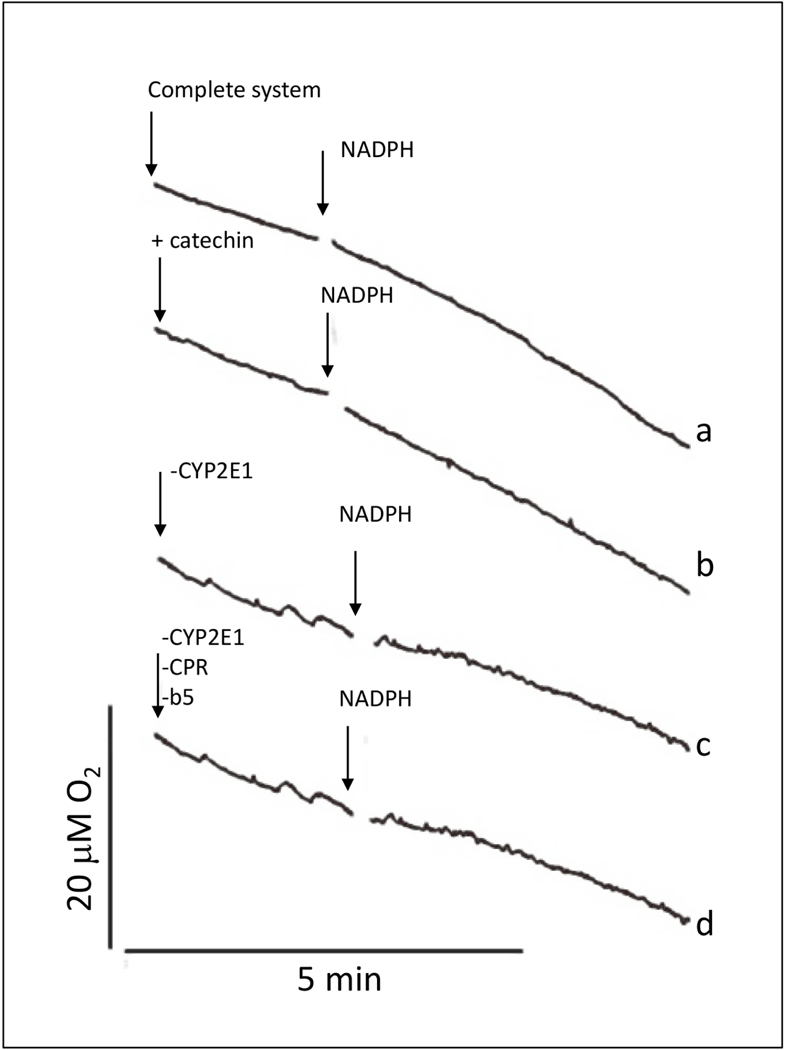
Effect of catechin on O2 consumption by the CYP2E1 + NADPH system, a) The complete system consisted of air-saturated 100 mM potassium phosphate buffer at pH 7.0 with 5 mM DTPA and 1 mg protein/mL of CYP2E1-expressing supersomes co-expressing NADPH cytochrome P450 reductase (CPR) and cytochrome b5 (b5); b) + catechin: catechin at 250 μΜ was added to the complete system; c) - CYP2E1: supersomes expressing only CPR and b5 replaced CYP2E1-expressing supersomes in the complete system; d) -CYP2E1, -CPR, -b5: supersomes devoid of CYP2E1, CPR and b5 replaced CYP2E1-expressing supersomes in the complete system. O2 concentration was recorded continuously using a Clark-type O2 electrode. In every experiment, NADPH at 2 mM was added at the time point indicated by the second arrow.
