Figure 1.
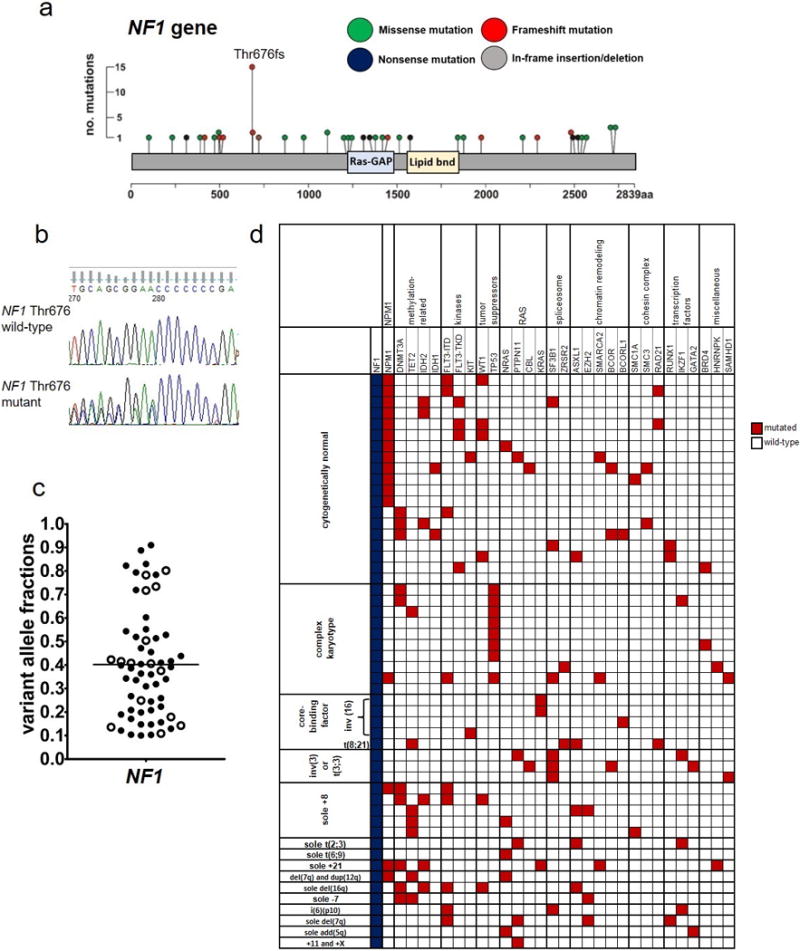
Mutations in the NF1 gene found in 1,021 patients with de novo acute myeloid leukemia. (a) Lollipop plots depicting 59 NF1 mutations detected in 52 patients. No. denotes number; aa, amino acid. (b) Sanger sequencing traces depicting examples of NF1 amino acid Threonine (Thr) 676 wild-type (top) and mutated (bottom) AML cases. (c) Beehive plot depicting variant allele fractions of the detected NF1 mutations. (d) Oncoprint of co-occurring mutations found in at least two AML patients with NF1 mutations (blue color), and of genes classified into the previously described functional groups.11 Each column represents an individual patient. Red color indicates that a gene was found to be mutated in the patient, white indicates wild-type status of the gene. The patients are grouped according to their pretreatment cytogenetic findings. The following genes also found to be mutated are not depicted in the oncoprint because they were detected in single patients (i.e., with a frequency below 2%): AXL and TYK2 (kinases); PHF6 (tumor suppressors); SRSF2 (splicesome); SF1 and SF3A3 (chromatin remodeling); STAG2 (cohesin complex); and CEBPA, ETV6 and NOTCH1 (transcription factors).
