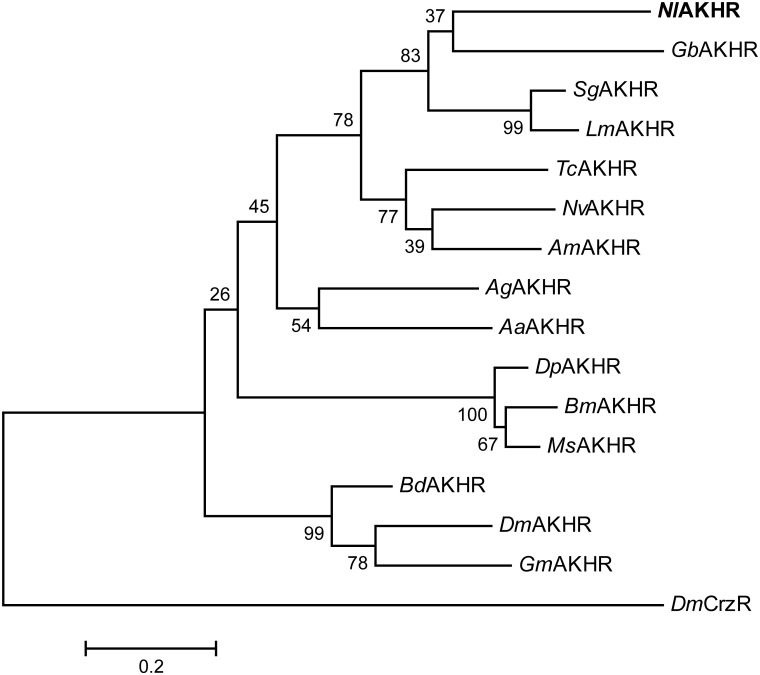
FIGURE 2.
Phylogenetic tree of NlAKHR and other insect AKHRs. The amino acid sequences of AKHR from N. lugens (NlAKHR, MH238458), Aedes aegypti (AaAKHR, CAY77164), Anopheles gambiae (AgAKHR, ABD60146), Apis mellifera (AmAKHR, NP_001035354), Bactrocera dorsalis (BdAKHR, AQX83416), Bombyx mori (BmAKHR, NP_001037049), Drosophila melanogaster (DmAKHR, NP_995639), Danaus plexippus (DpAKHR, OWR46881), Glossina morsitans (GmAKHR, AEH25943), Gryllus bimaculatus (GbAKHR, ADZ17179), Locusta migratoria (LmAKHR, ANW09575), Manduca sexta (MsAKHR, AEH25943), Nasonia vitripennis (NvAKHR, NP_001161243), Schistocerca gregaria (SgAKHR, AVG47955), and Tribolium castaneum (TcAKHR, NP_001076809) were aligned using the ClustalW program. The tree was constructed by MEGA 6 using the Maximum Likelihood (ML) method with 1000 bootstrap replicates. D. melanogaster Corazonin receptor (DmCrzR, AF373862) was used as external group. The scale bar represents 0.2 amino acid substitutions per site.