Figure 5.
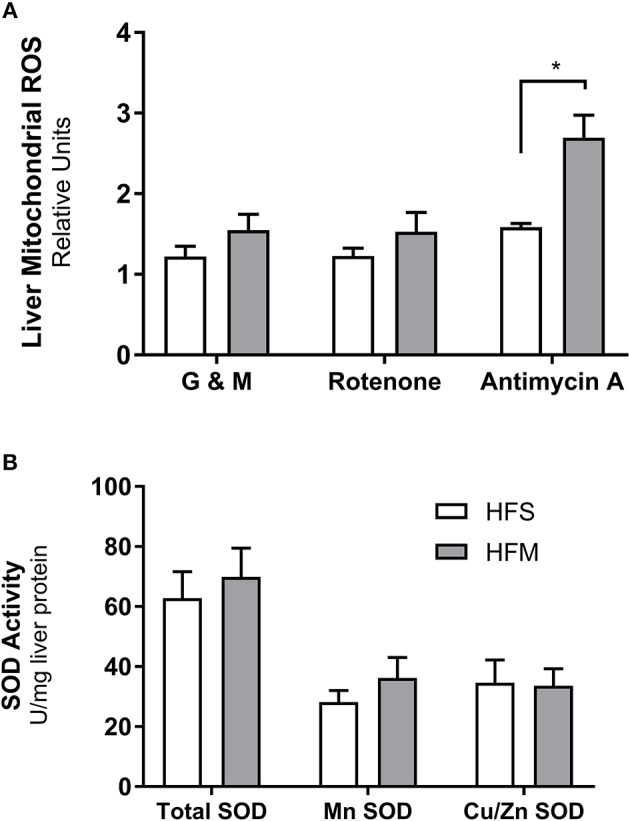
Detection of reactive oxygen species production and superoxide dismutase enzyme activity from liver homogenates. Following control (saline) or MSC therapy, liver homogenates were used to quantify the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and the free radical scavenging enzyme superoxide dismutase (SOD). (A) Relative rates of H2O2 production as a function of ROS generation. Mitochondria isolated from liver tissue were stimulated in the presence of ADP under a variety of conditions including: glutamate and malate as substrates (G & M; complex I), rotenone as an inhibitor (complex I), and antimycin as an inhibitor (complex III). (B) SOD enzyme activity measured from liver homogenates. SOD activity is stratified into manganese (Mn) or zinc and copper (Zn and Cu) fractions, with total representing both portions combined. SOD data are normalized to mg of liver protein and ROS data are normalized to mg of mitochondrial protein. All data are mean ± SEM with n = 8 for both groups. *Denotes statistical significance at p < 0.05.
