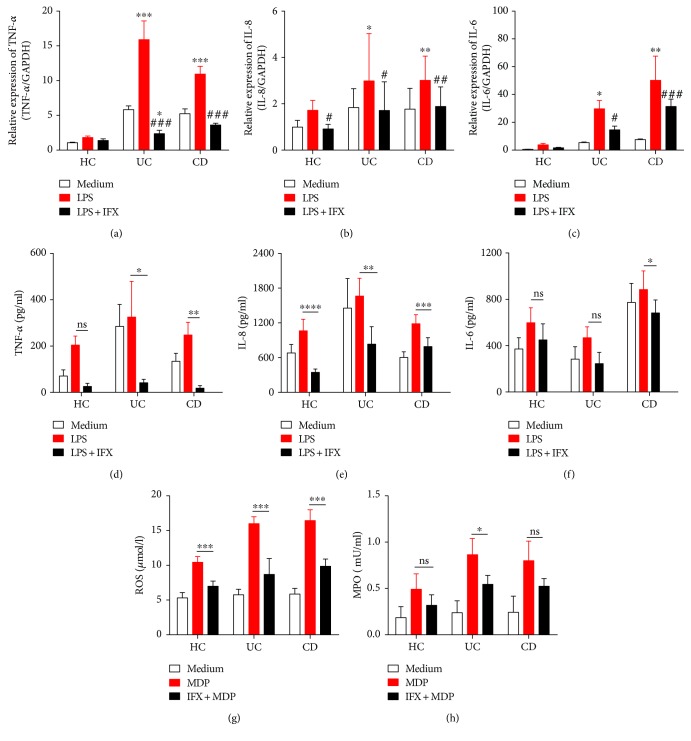
Figure 4.
Anti-TNF-α therapy inhibits peripheral neutrophils to produce proinflammatory cytokines, chemokines, ROS, and MPO. Peripheral neutrophils (5 × 106) from healthy donors (n = 10), patients with active CD (n = 10), and active UC (n = 10) were stimulated by LPS (200 ng/ml) and incubated with or without IFX (50 μg/ml) for 3 h. Cells were collected and expressions of TNF-α (a), IL-8 (b), and IL-6 (c) were detected by qRT-PCR. Peripheral neutrophils (2 × 106) from healthy donors (n = 6), patients with active CD (n = 11), and patients with active UC (n = 4) were simulated with LPS (200 ng/ml) and incubated with or without IFX (50 μg/ml) for 3 h. Culture media were replenished and incubated for another 24 h. Supernatants and protein production of TNF-α (d), IL-8 (e), and IL-6 (f) were measured by ELISA. Peripheral neutrophils (1 × 104) isolated from healthy donors (n = 5), patients with active CD (n = 5), and patients with active UC (n = 5) were measured for ROS (h) and MPO (i) with Amplex Red Hydrogen Peroxide Assay Kit. ∗ P < 0.05, ∗∗ P < 0.01, and ∗∗∗ P < 0.001 compared with medium control and # P < 0.05, ## P < 0.01, and ### P < 0.001 compared with LPS stimulation.