Figure 1: An AOP for embryonic vascular disruption.
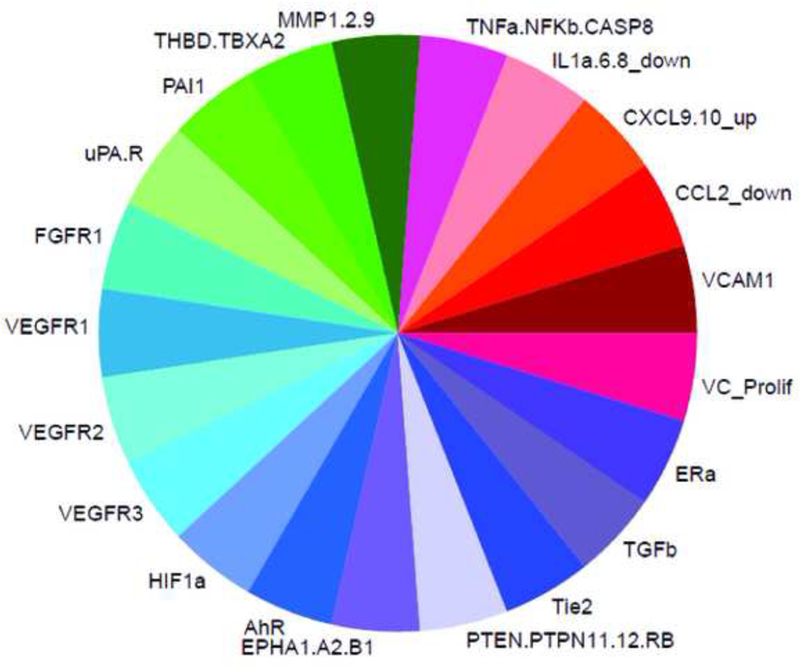
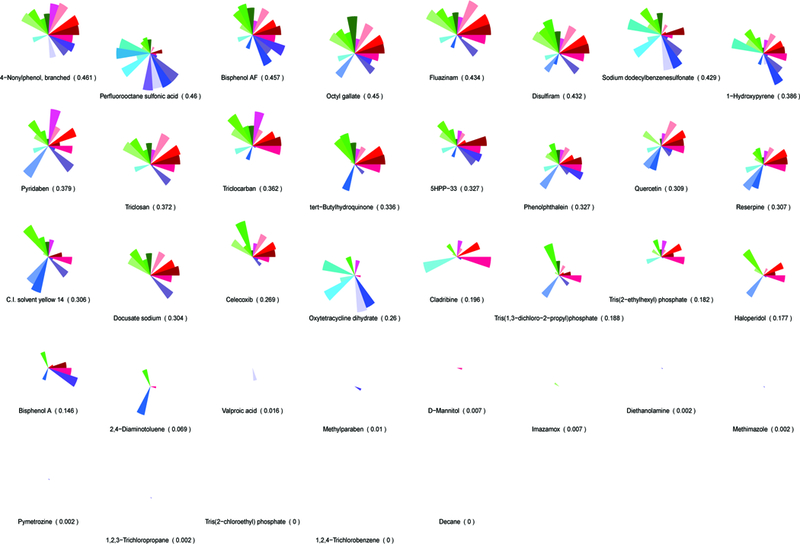
A predictive toxicity model was generated to group chemicals by their in vitro bioactivity profile and look for signatures that correlate with in vivo toxicity. (A) An AOP for embryonic vascular disruption was constructed by identifying initial molecular targets that are linked to developmental angiogenesis and coarsely map to 124/821 human in vitro ToxCast assays. ToxCast assays (124) mapping to 30 molecules are included in the ToxPi for putative vascular disrupting compounds (pVDCs). (B) The signature was used to rank order 1060 ToxCast chemicals and a 37 member chemical test set was selected. CASP8 (Caspase 8); CCL2 (chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 2); CXCL9.10 (C-X-C motif chemokine 9 and 10); EPHA1.A2.B1 (Ephrin receptor type A1, A2, and B2); ERa (Estrogen receptor alpha); FGFR (Fibroblast growth factor receptor); HIF1a (Hypoxia inducible factor 1 alpha); IL1a.6.8 (Interleukin 1a, 6, and 8); MMP1.2.9 (Matrix metalloproteinase 1, 2, and 9); NFkB (Nuclear factor kappa B); PAI1 (Plasminogen activator 1); PTEN (Phosphatase and tensin homolog); PTPN11.12 (Protein tyrosine phosphatase non-receptor type 11 and 12); PTPRB (Protein tyrosine phosphatase receptor type B); TBXA2 (Thromboxane A2): THBD (Thrombomodulin); Tie2 (TEK tyrosine kinase); TNFa (Tumor necrosis factor alpha); TGFb (Transforming growth factor beta); uPA (Urokinase-type plasminogen activator); uPAR (Urokinase receptor); VEGFR1.2.3 (Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 1, 2, and 3); VCAM1 (vascular cell adhesion protein 1); VC_Prolif (Vascular cell proliferation).
