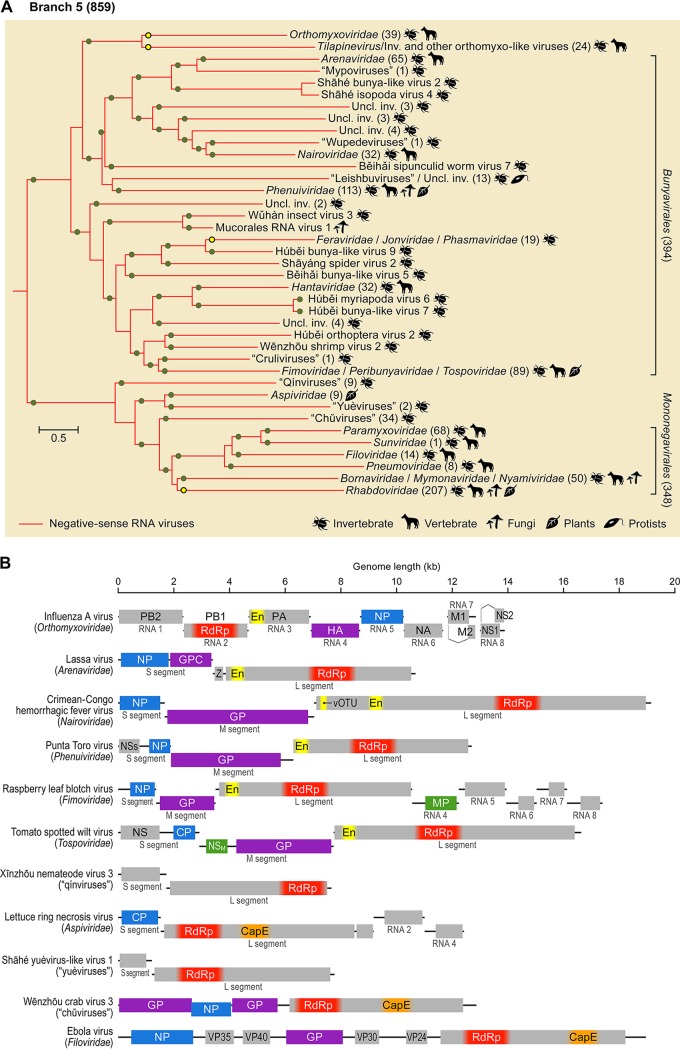
FIG 6.
Branch 5 of the RNA virus RNA-dependent RNA polymerases (RdRps): −RNA viruses. (A) Phylogenetic tree of the virus RdRps showing ICTV-accepted virus taxa and other major groups of viruses. Approximate numbers of distinct virus RdRps present in each branch are shown in parentheses. Symbols to the right of the parentheses summarize the presumed virus host spectrum of a lineage. Green dots represent well-supported (≥0.7) branches, whereas yellow dots correspond to weakly supported branches. Inv., viruses of invertebrates (many found in holobionts, making host assignment uncertain); uncl., unclassified. (B) Genome maps of a representative set of branch 5 viruses (drawn to scale) showing color-coded major conserved domains. Where a conserved domain comprises only a part of the larger protein, the rest of this protein is shown in light gray. The locations of such domains are approximated (indicated by fuzzy boundaries). CapE, capping enzyme; CP, capsid protein; EN, “cap-snatching” endonuclease; GP, glycoprotein; GPC, glycoprotein precursor; HA, hemagglutinin; M, matrix protein; MP, movement protein; NA, neuraminidase; NP, nucleoprotein; NS, nonstructural protein; NSM, medium nonstructural protein; NSs, small nonstructural protein; PA, polymerase acidic protein; PB, polymerase basic protein; vOTU, virus OTU-like protease; VP, viral protein; Z, zinc finger protein.