Figure 4.
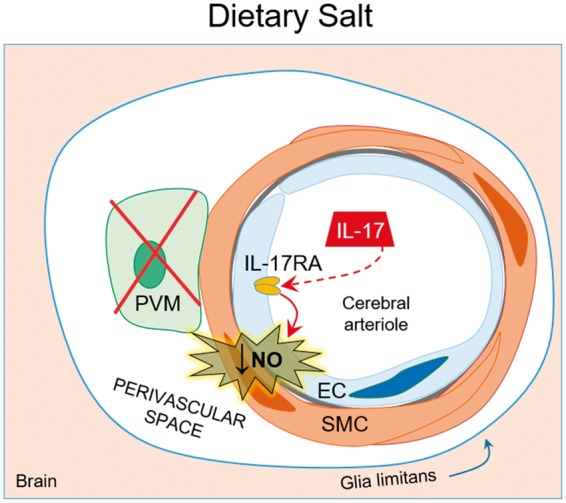
Dietary salt induces endothelial dysfunction and cognitive deficits. High dietary salt stimulates Th17 polarization in the gut leading to increased circulating IL-17. IL-17 acts on the cerebral endothelium to induce inhibitory phosphorylation of eNOS through Rho-kinase, thus reducing NO production and bioavailability. The resulting endothelial dysfunction in the cerebral vasculature is associated with cognitive impairment. Remarkably, neurovascular coupling is not affected. Of note, PVM do not play a role in the cerebrovascular dysfunction of dietary salt.
