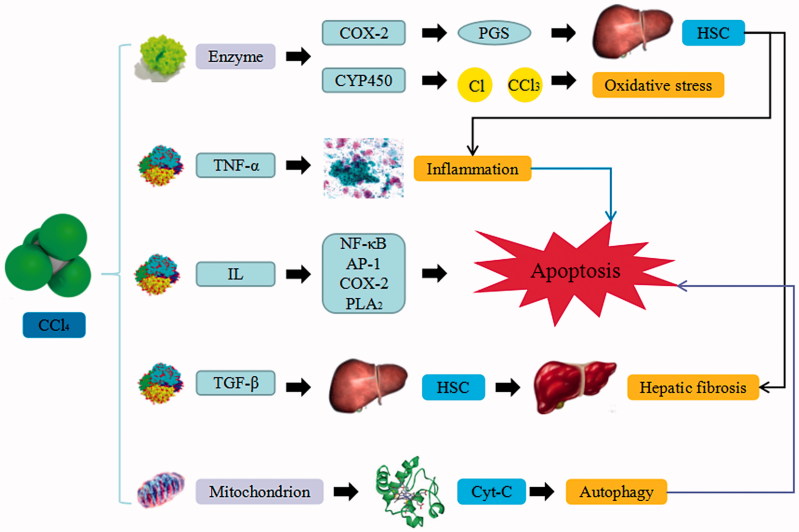
Figure 1.
CCl4-induced liver injury. CCl4 trigger the continuous development of hepatocyte injury by inducing cell stress via inflammation, macrophages activation, mitochondrion path, and oxidative stress, resulting in apoptosis, hepatic fibrosis, and liver injury. COX-2: epoxide hydrolase; PGs: prostaglandins; HSC: hepatic stellate cells; CYP450: cytochrome P450; TNF-α: tumor necrosis factor α; IL: interleukin; NF-κB: nuclear factor κB; AP-1: activated protein transcription factor 1; PLA2: phosphatase A2; TGF-β: transforming growth factor β; Cyt-C: cytochrome C.