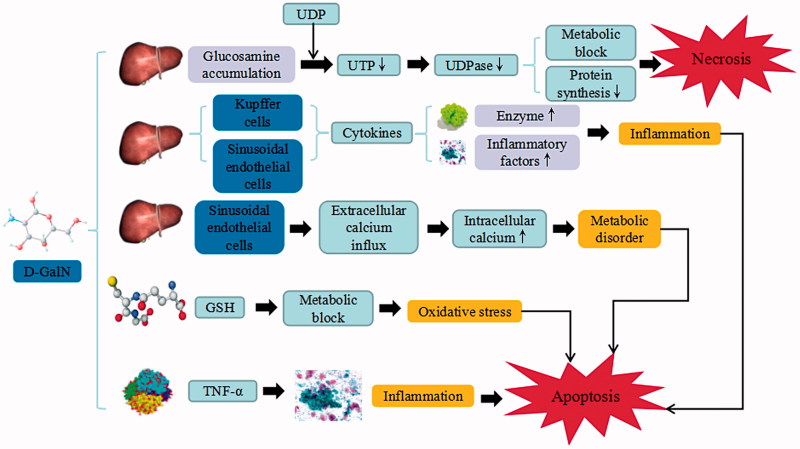
Figure 2.
d-GalN-induced liver injury. d-GalN trigger the continuous development of hepatocyte injury by inducing cell stress via inflammation, metabolic disorder, and oxidative stress, resulting in necrosis, apoptosis, autophagy, and liver injury. UDP: uridine diphosphate; UTP: uridine triphosphate; UDPase: UDP-glucose pyrophosphorylase; GSH: glutathione; TNF-α: tumor necrosis factor α.