Figure 6.
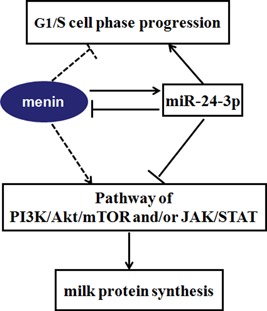
MiR‐24‐3p regulates cell proliferation and milk protein synthesis in mammary epithelial cells through cooperatively acting with MEN1/menin. MiR‐24‐3p positively regulates the proliferation of mammary epithelial cells, promoting the G1/S cell phase progression. While, MEN1/menin was found, in our previous study (Li et al., 2017), negatively control the proliferation of at G1/S phase progression, causing cell growth arrest. This is contributed to the negative feedback controlling model between miR‐24‐3p and MEN1/menin. The dynamic balance model between miR‐24‐3p and MEN1/menin also make an opposite impacts on milk protein synthesis of mammary epithelial cells through PI3K/AKT/mTOR and/or JAK/STAT signaling pathway. The solid line represents fluxes found in the current study; the dotted line represents previously found effects or fluxes (Li et al., 2017). The arrows indicate the positive regulation, and the blunt‐ended ones indicate the negative regulation. AKT: protein kinase B; JAK: Janus kinase; MEN1: multiple endocrine tumor type 1; mTOR: mammalian target of rapamycin; PI3K: phosphatidylinositol‐3‐kinase; STAT: signal transducer and activators of transcription [Color figure can be viewed at wileyonlinelibrary.com]
