Figure 2.
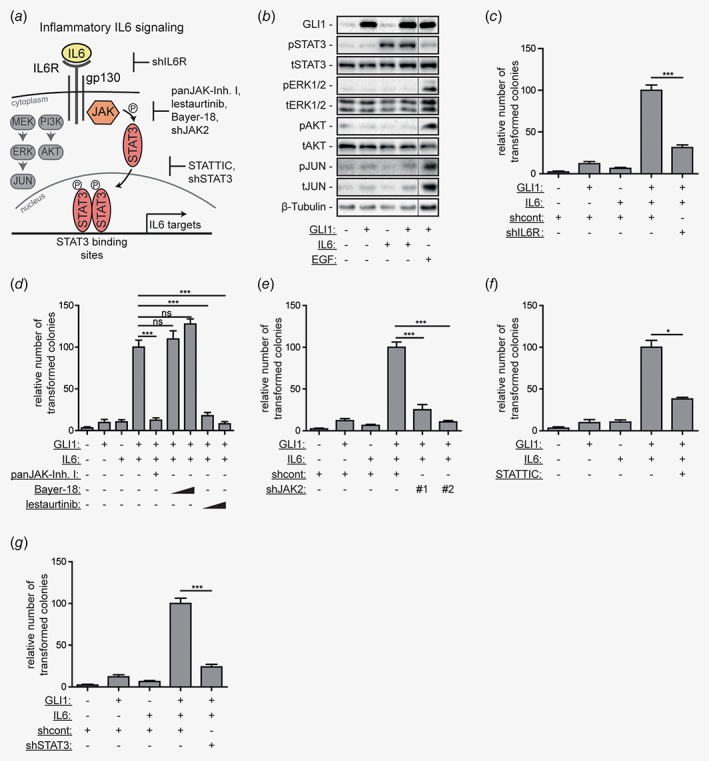
IL6/JAK2/STAT3 signaling cooperates with HH/GLI in oncogenic transformation.(a) Illustration of IL6 signaling and downstream pathway activation. Binding of IL6 to its receptor can activate at least three downstream signaling cascades: JAK/STAT3, MEK/ERK/JUN and PI3K/AKT signaling. In the context of malignant transformation, IL6 induces JAK/STAT3 activation. The genetic and pharmacologic approaches to inhibit IL6 signaling effectors are depicted.(b) Western blot analysis of GLI1 expressing human HaCaT keratinocytes treated with IL6, or 10 ng/ml EGF. β‐tubulin served as loading control. Fine black lines indicate cropping of intermediate lanes from the same Western blots. p, phospho; t, total;(c–g) Quantitative analysis of in vitro transformation assays using HaCaT keratinocytes. Cells were treated either with solvent, Dox to induce GLI1, IL6 or Dox and IL6. Additionally, double‐stimulated cells (+GLI1;+IL6) were treated as follows: (c) with shRNA against IL6R (shIL6R, shRNA #1 in Supporting Information, Fig. S1 a), (d) with panJAK‐Inh I (1 μM), Bayer‐18 (100 nM and 300 nM) or lestaurtinib (100 nM and 300 nM), (e) with shRNA constructs against JAK2 (shJAK2#1, shJAK2#2), (f) with STATTIC (1 μM) or (g) with shRNA against STAT3 (shSTAT3). ns, not significant; shcont, scrambled nontarget control shRNA; Statistical analysis by Student's t test; ***p < 0.001; *p < 0.05.
