Figure 3.
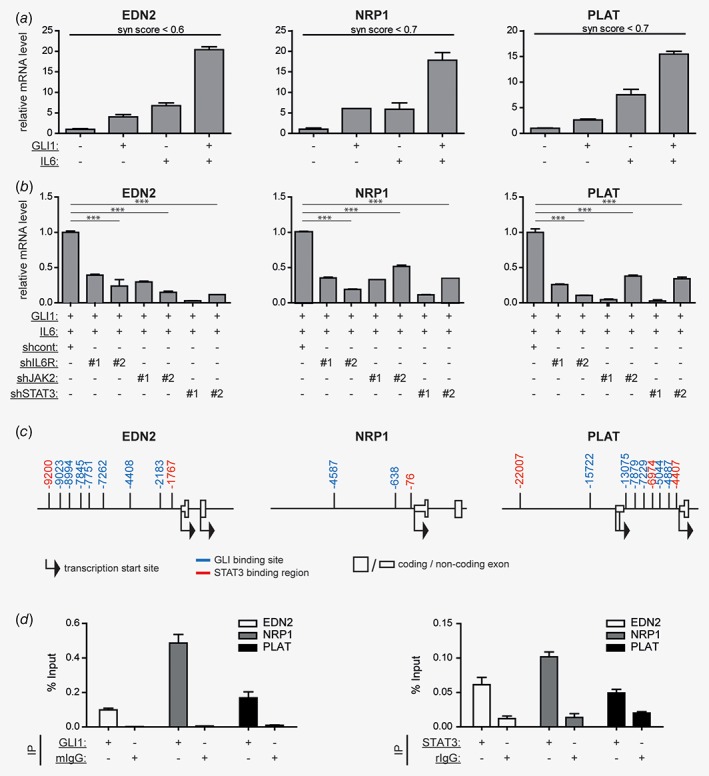
Integration of HH‐IL6 signaling at cis‐regulatory regions of common HH‐IL6 target genes.(a) mRNA expression analysis by qPCR of selected HH‐IL6 target genes (EDN2, NRP1, PLAT) in human HaCaT keratinocytes in response to Dox‐induced GLI1 expression, IL6 treatment or a combination of both. Synergy (syn) score values of ≤0.9 indicate synergistic cooperation of simultaneous HH‐IL6 signaling.(b) qPCR mRNA expression analysis of HH‐IL6 target genes in human HaCaT keratinocytes in response to GLI1 expression, IL6 stimulation and additional knockdown of IL6R (shIL6R#1, shIL6R#2), JAK2 (shJAK2#1, shJAK2#2) or STAT3 (shSTAT3#1, shSTAT3#2). Signals are relative to double‐stimulated cells transduced with shcont non‐target shRNA. shcont, scrambled nontarget control shRNA; ***p < 0.001;(c) In silico analysis of the cis‐regulatory region of selected HH‐IL6 target genes (EDN2, NRP1, PLAT) for the presence of STAT3 binding regions and putative GLI binding sites. Numbers show the start position of GLI binding sites (blue) and STAT3 binding regions (red) relative to the transcriptional start site (TSS).(d) ChIP analysis of selected HH‐IL6 target genes (EDN2, NRP1, PLAT) for GLI1 (left) and STAT3 binding (right). Human HaCaT keratinocytes expressing Dox‐inducible MYC‐tagged GLI1 treated with IL6 were analyzed. Mouse IgG (mIgG) or rabbit IgG (rIgG) served as negative controls.
