Figure 2.
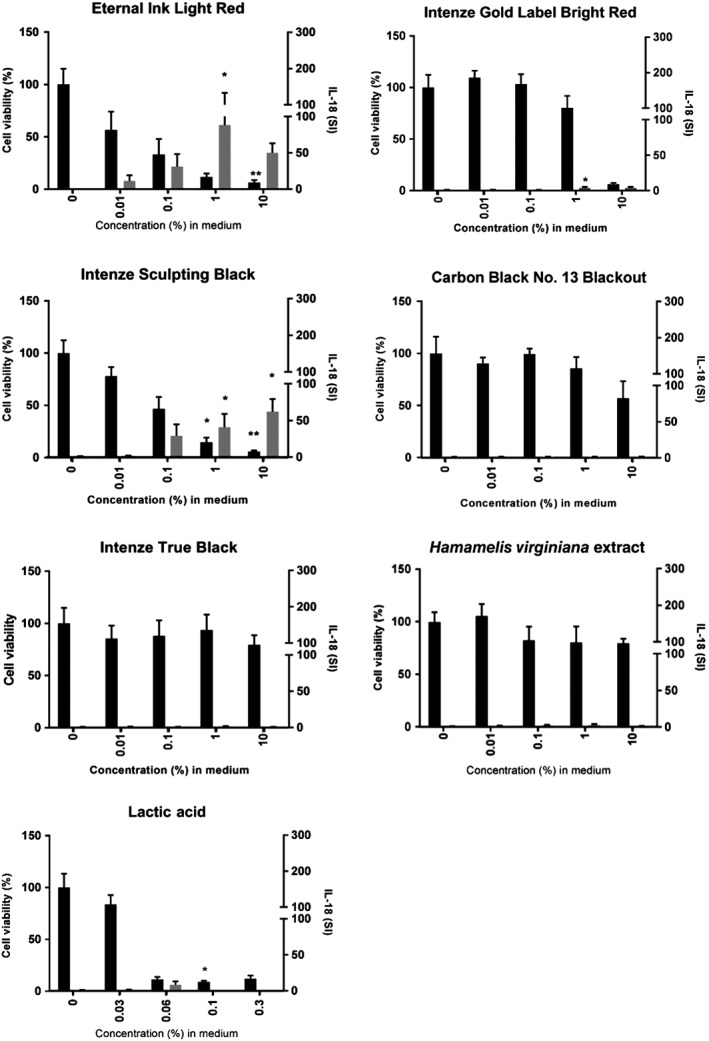
Tattoo inks are cytotoxic and result in interleukin (IL)‐18 release from reconstructed human skin (RHS). RHS was exposed to test substances for 24 hours, culture supernatants were analysed with a specific IL‐18 enzyme‐linked immunosorbent assay, and RHS cell viability was then determined with the thiazolyl blue tetrazolium bromide assay. IL‐18 stimulation index (SI) (grey bars) and cell viability (black bars) are shown as mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM), with each experiment (n) representing a different batch of RHS constructed from a different donor skin for Eternal Ink Light Red (n = 5), Intenze Gold Label Bright Red (n = 5), Intenze Sculpting Black (n = 5), Carbon Black No. 13 Blackout (n = 4), Intenze True Black (n = 4), Hamamelis virginiana extract (n = 4), and lactic acid (n = 3). Statistical significance was determined with 1‐way ANOVA followed by Dunn's multiple comparison test. *P < .05 and **P < .01 as compared with the vehicle‐exposed RHS
