Figure 2.
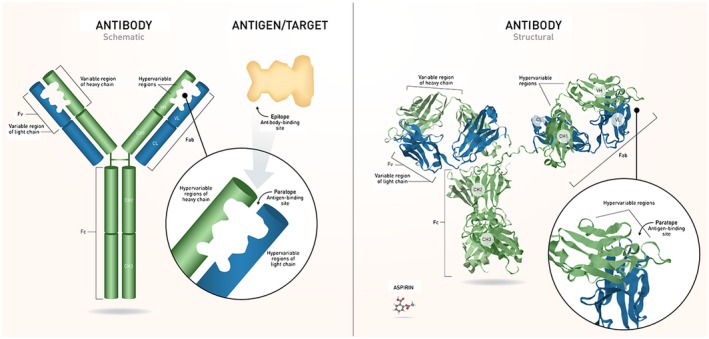
Structure of Ig. Antibodies are composed of 2 identical heavy and light chains that join to form the characteristic “Y” shape. The light chain contains 1 variable domain and 1 constant domain. The heavy chain contains 1 variable domain and 3 constant domains. Each antibody has an Fc region – the stem of the “Y,” which determines the effector function – and a Fab domain, the arms of the “Y.” The variable domains of each chain include a framework region and 3 CDRs, also referred to as hypervariable regions. The set of CDRs constitutes the paratope, the antigen‐binding site that recognizes the epitope of a specific antigen. IgG (~150,000 Da) is shown next to aspirin (~180 Da) for a comparison between antibodies and small molecules. CH = heavy chain constant; CL = light chain constant; FV = variable fragment; VH = heavy chain variable; VL = light chain variable. [Color figure can be viewed at https://wileyonlinelibrary.com] [Correction added after first online publication on November 26, 2018: Figure swapped with Figure 1.]
