Figure 4. Generation of dasatinib resistant pre-BCR+ human ALL cells.
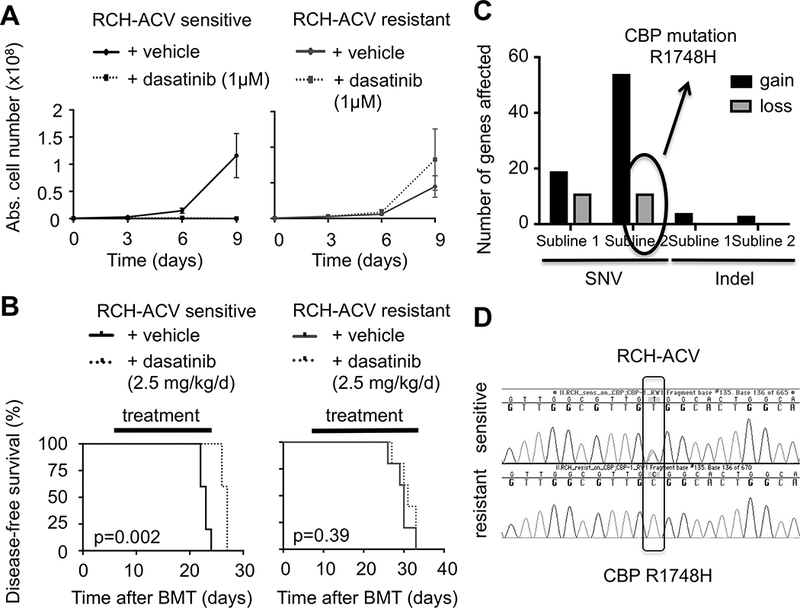
(A) Dasatinib-sensitive (left panel) and –resistant (right panel) RCH-ACV cells were cultured in the presence of vehicle or 1 μM dasatinib for nine days. Cell proliferation was assessed every three days by trypan blue assay. Data represent the mean ±SEM from four independent experiments. (B) Kaplan-Meier curve shows disease-free survival of NSG mice xeno-transplanted with dasatinib-sensitive (left panel) and –resistant (right panel) RCH-ACV cells. Recipients were treated with either vehicle or dasatinib for 20 days. Statistical analysis by log rank test. (C) Analysis of number of genes affected by SNV and indels in dasatinib-resistant compared to dasatinib-sensitive RCH-ACV sublines in RNA-seq data. Gain indicates presence and loss indicates absence of sequence aberrations in dasatinib-resistant sublines. (D) Chromatograms from Sanger sequencing show validation of CBP R1748H SNV identified by RNA-seq detected in dasatinib-sensitive but absent in dasatinib-resistant RCH-ACV cells.
