Figure 3.
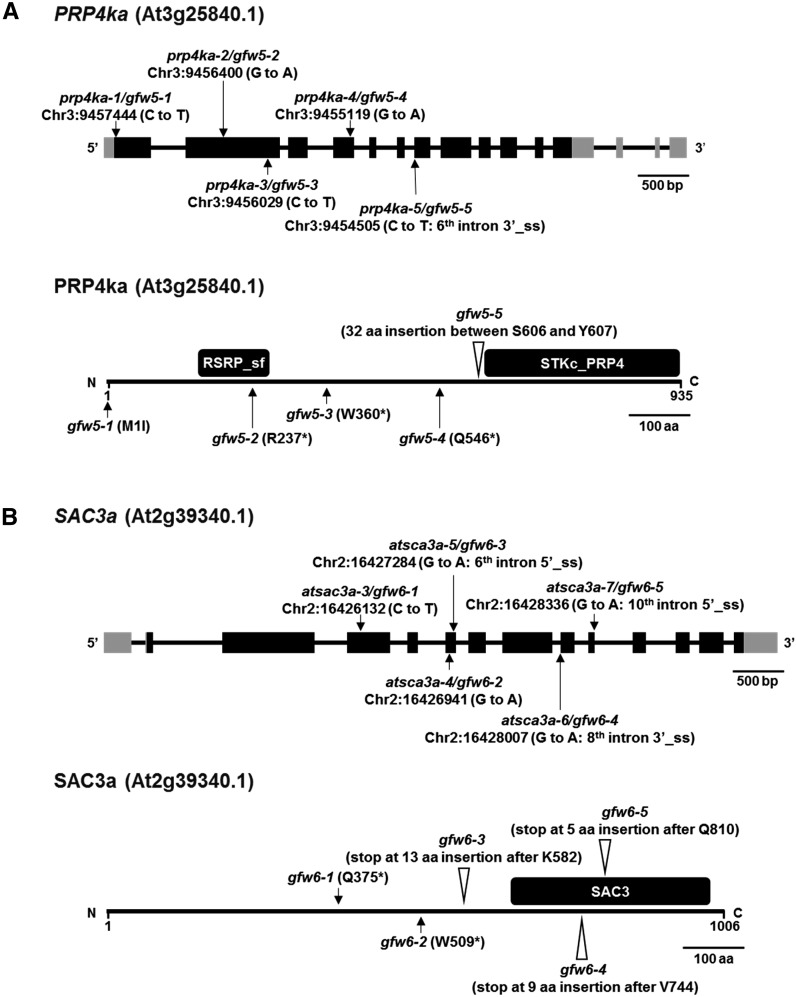
PRP4KA and SAC3A gene structures, positions of mutations, and protein domains. (A) The pre-mRNA of PRP4KA (At3g25840) is alternatively spliced. Two splice variants are annotated in TAIR (http://www.arabidopsis.org/index.jsp) and 14 splice variants are annotated in AtRTD2 (Zhang et al. 2017). The reference transcript isoform At3g25840.1 encodes a 935 amino acid protein that contains RS protein (RSRP) superfamily domain and a catalytic domain of the serine/threonine kinase, pre-mRNA processing factor 4 (STKc_PRP4) domain (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/). We identified the following prp4ka alleles in our screen: prp4ka-1 (M1I), prp4ka-2 (R237*), prp4ka-3 (W360*), prp4ka-4 (Q546*), and prp4ka-5 (splice-site acceptor, sixth intron) (Figure S2). All of these alleles, which encode defective mRNAs or, in one case, abolishes initiation of translation at the normal ATG start codon (the next methionine codon is 300 bp downstream), are likely to be nulls. (B) SAC3A (At2g39340) encodes a 1066 amino acid protein containing a conserved SAC3/GANP/THP3 domain (http://www.arabidopsis.org/). In budding yeast, this domain in the SAC3 protein integrates interactions between other proteins in the TREX complex that couples transcription and mRNA export (https://www.ebi.ac.uk/interpro/). We identified the following sac3a alleles: sac3a-3 (Q375*), sac3a-4 (W509*), sac3a-5 (splice-site donor, sixth intron), sac3a-6 (splice-site acceptor, eighth intron), and sac3a-7 (splice-site donor, 10th intron). The sac3a alleles all encode defective mRNAs and are likely to be nulls. Chr3, chromosome 3; 3′_ss, alternative 3′ splice-site acceptor; 5′_ss, alternative 5′ splice-site donor.