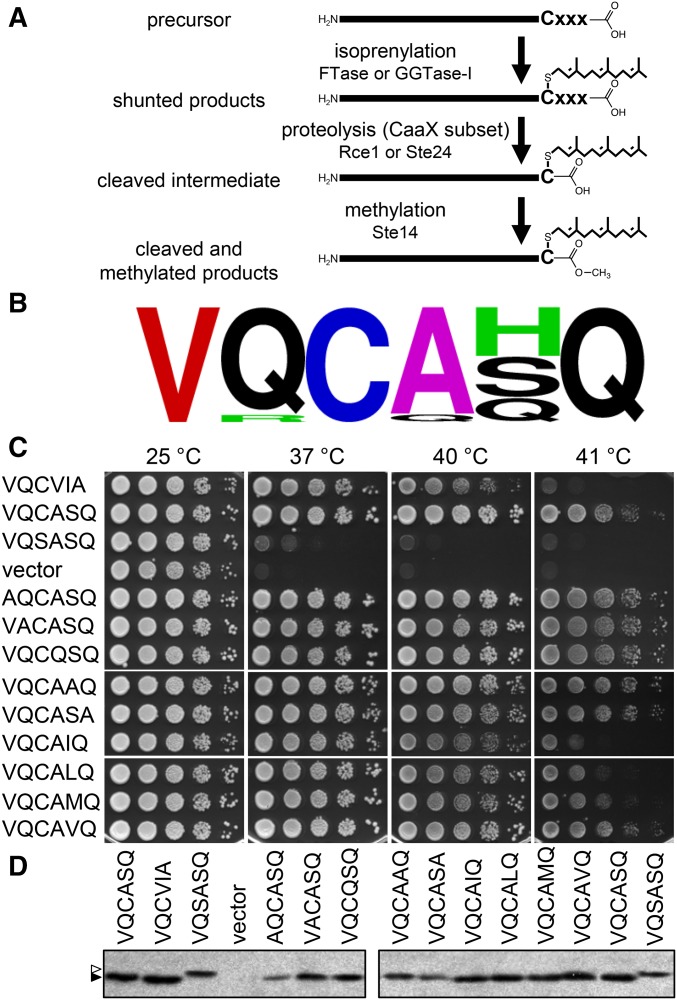
Figure 1.
Site-directed mutation of the Ydj1p Cxxx motif reveals flexibility in sequence requirements for functional levels of isoprenylation. (A) The Cxxx motif directs protein isoprenylation. Both farnesyl (C15) and geranylgeranyl (C20) can be added to Cxxx proteins; only C15 addition is shown for clarity. The isoprenylated species is either the endpoint modification (e.g., Ydj1p; shunted proteins) or an intermediate that is additionally modified by proteolysis and carboxymethylation (e.g., K-Ras4b; traditional CaaX proteins). Not shown are more extensive modifications that can also occur, such as palmitoylation (e.g., H- and N-Ras) or distal proteolysis (e.g., lamin A; yeast a-factor). (B) WebLogo frequency analysis of the last seven amino acids associated with 14 Ydj1p homologs retrieved from the Homologene Database (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/homologene). Color scheme is as described in Materials and Materials and Methods. See Figure S1 for specific sequence details. (C) Ydj1p mutants were evaluated for their ability to support high-temperature yeast growth. yWS304 yeast (ydj1∆) expressing the indicated plasmid-encoded Ydj1p mutant were cultured in selective SC-uracil media and pinned as 10-fold serial dilutions onto nonselective YPD; the leftmost spot in each panel is undiluted. Plates were incubated at the indicated temperature as described in Materials and Methods. (D) The Ydj1p mutants indicated in C were expressed in yWS304 (ydj1∆) and cell lysates evaluated by anti-Ydj1p immunoblot. The specific plasmids used for Figure 1 are listed in Table S2. Unmodified Ydj1p (open triangle) migrates at a larger apparent kDa than prenylated Ydj1p (solid triangle).