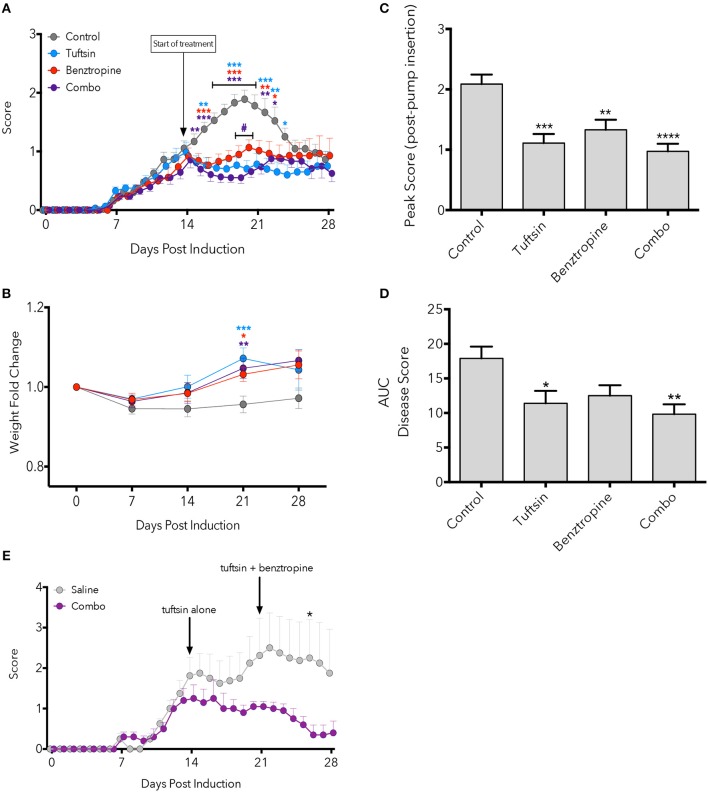
Figure 1.
Combinatorial therapy attenuates EAE. EAE was induced by subcutaneous injection of MOG35−55 in CFA and i.p. injections of pertussis toxin on Day 0 and 2. At Day 14 post-MOG immunization, a mini-osmotic pump containing tuftsin, benztropine, or both drugs were implanted subcutaneously in treated groups. Mice were euthanized at either day 21 or 28 for histological analysis. Comparisons are between control and tuftsin (blue asterisks), control and benztropine (red asterisks), control and combo (purple asterisks), and benztropine and combo (purple pound sign) (A). Weights were recorded weekly and compared between control and all treated groups with asterisks indicating significance as stated above (B). Weights are plotted as fold change from Day 0 weight. Peak score (C) and area under the curve (D) were compared between all groups. EAE was induced as in (A) and mini-osmotic pumps were inserted on Day 14 containing tuftsin alone or saline. Pumps were replaced on Day 21 with benztropine added to treated mice. Arrows denote day of pump insertion and pump replacement (E). All data are mean ± SEM. n = 5–29 (A–D), n = 4–5 (E), analyzed by two-way ANOVA, *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001.