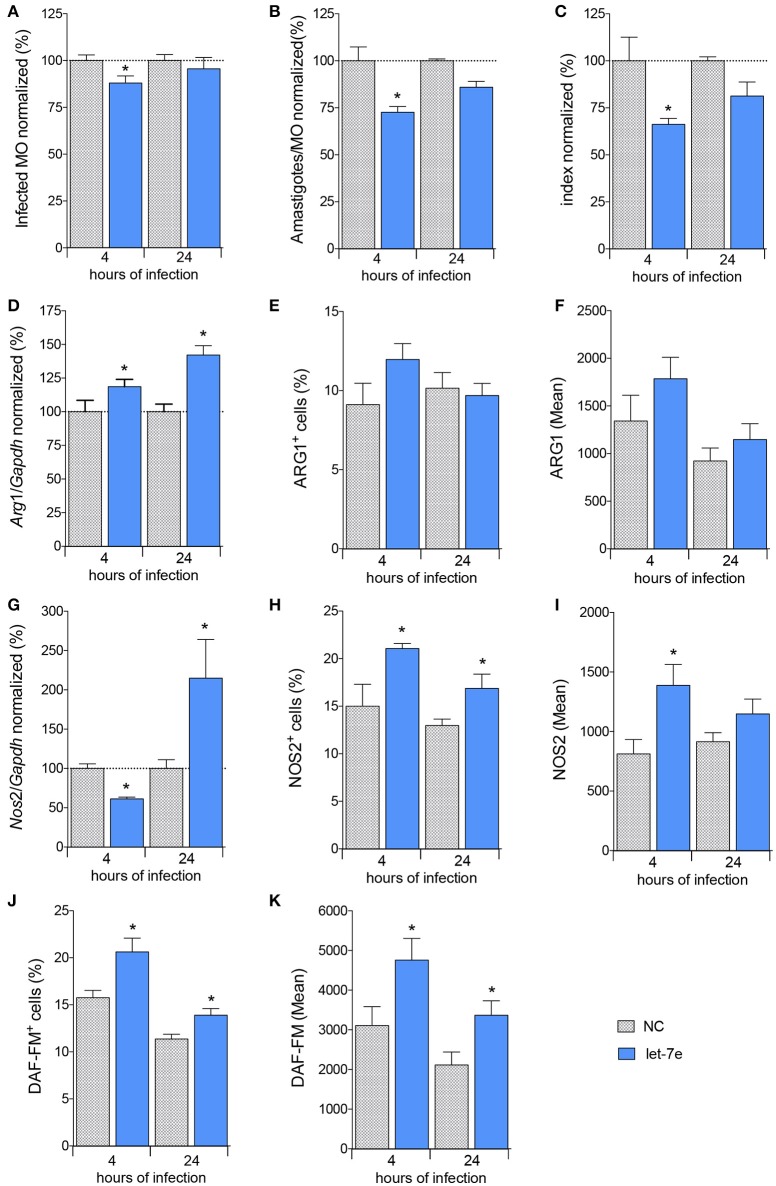
Figure 5.
Inhibition of let-7 increases differential gene expression and reduces L. amazonensis infectivity. BMDMs were transiently transfected with 100 nM negative control (NC—filed patterned bar) or let-7e-5p inhibitor (let-7e—blue bar). Twenty-four hours after transfection, the cells were co-cultivated with L. amazonensis (MOI 5:1) for 4 h, and the cultures were then washed. Four and 24 h after infection, the samples were analyzed for infectivity under the microscope by counting the numbers of infected macrophages (A), amastigotes per infected macrophage (B), and infectivity index (C) (n = 1,000 macrophages/treatment). RT-qPCR was used to determine the total levels of the Arg1 (D) and Nos2 (G) mRNAs. The percentage of cells expressing ARG1 (E) or NOS2 (H) and fluorescence intensity of ARG1 (F) or NOS2 (I) staining were determined using flow cytometry. The percentage of NO-producing cells (DAF-FM+ cells—K) and fluorescence intensity of NO production per cell (DAF-FM mean—J) were also determined using flow cytometry. The values were normalized to the average values of NC-transfected and infected macrophages (100%). Each bar represents the average ± SEM of the values obtained from three independent experiments (n = 4–8). Statistical significance was determined using two-tailed Student's t-test. *p < 0.05 compared to NC-transfected, infected macrophages.