Figure 7. Possible mechanism of ELC-2 regulating behavioral plasticity in response to heat stress. Basal state:
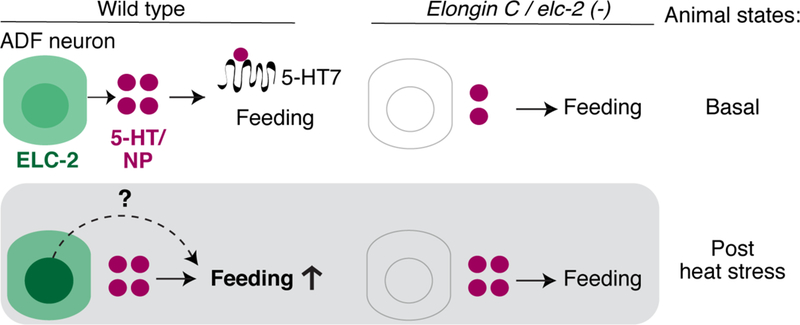
ELC-2 is expressed in ADF sensory neurons, which release serotonin and neuropeptides through dense-core vesicles. Serotonin from ADF and from other neurons (top circles) regulate pharyngeal pumping feeding behavior. The basal state in elc-2 mutants is different from wild type, with reduced dense core vesicle release, but its basal feeding behavior is normal. Post stress state: Heat stress experience induces both a dynamic localization of ELC-2 in ADF nucleus, and increased feeding in the animal. Serotonin binds metabotropic receptor SER-7/5-HT7 (scribble; omitted in top panels) to regulate stimulus-dependent pharyngeal pumping feeding behavior. elc-2 and other ECS mutants are unable to alter feeding behavior in response to stress. The role of ELC-2 dynamic redistribution is unclear, and may serve to alter the activity of ELC-2 in the cytoplasm to increase feeding (dotted line) and/or contribute to a parallel function in the nucleus that is initiated by noxious heat. See also Figures 4 and S4–5.
