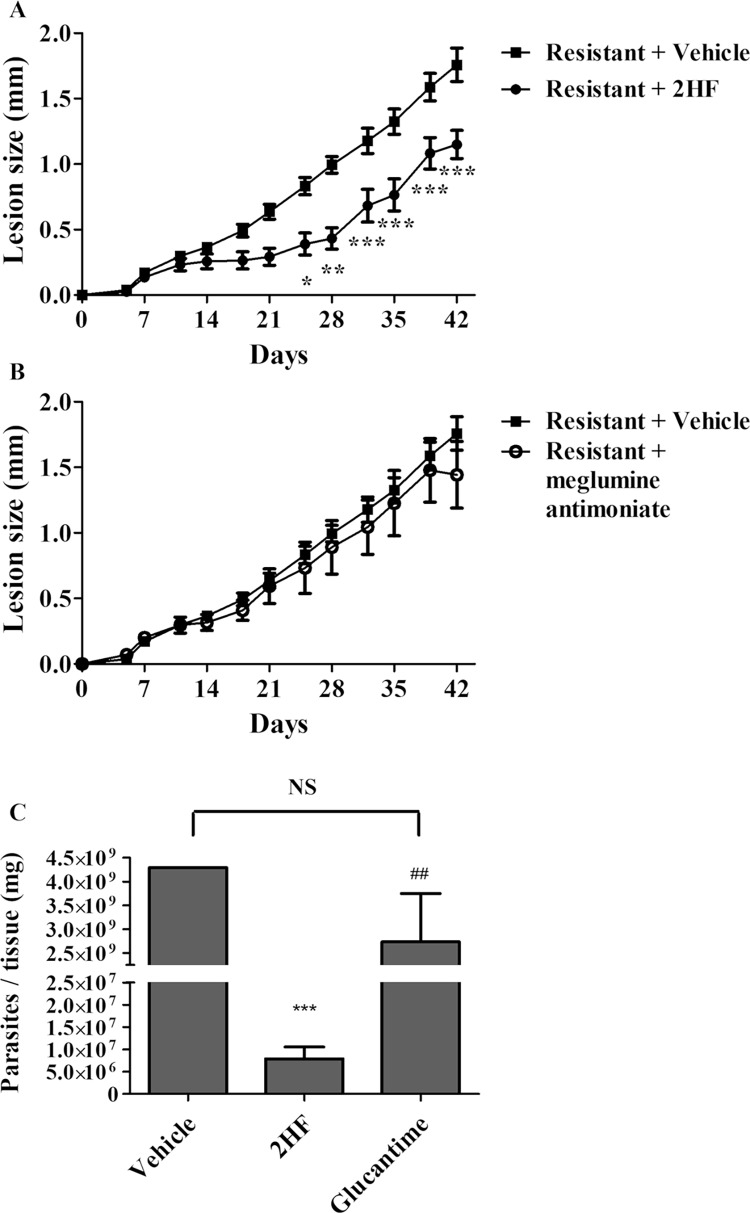
Fig 6. Leishmanicidal effect of 2HF and meglumine antimoniate in antimony-resistant L. amazonensis -infected BALB/c mice.
BALB/c mice were infected in the right ear with 4 × 106 antimony-resistant L. amazonensis promastigotes. Panel A: Lesion development on the animals treated orally with 2HF (50 mg/kg/day). Panel B: Lesion development on the animals treated intraperitoneally with meglumine antimoniate (100 mg/kg/day). The untreated mice (control group) were treated with an oral suspension added to DMSO (0.2% v/v) (2HF vehicle). The treatment started seven days post-infection and was given once daily seven times per week until the end of the experiment (day 42). Panel C: Parasite burden of the L. amazonensis-infected BALB/c mice untreated or treated with 2HF (50 mg/kg/day) or meglumine antimoniate (100 mg/kg/day). Ear parasite loads were determined via a limiting dilution assay. Data are expressed as the means ± standard errors. These data represent one independent experiment with five mice per group each (n = 5). *, ** and *** indicate significant differences relative to the control group (p < 0.05; p < 0.01 and p < 0.001, respectively) and ## indicate significant differences relative to 2HF (p < 0.01); 2HF = 2’-Hydroxyflavanone; ns = No statistical significance.