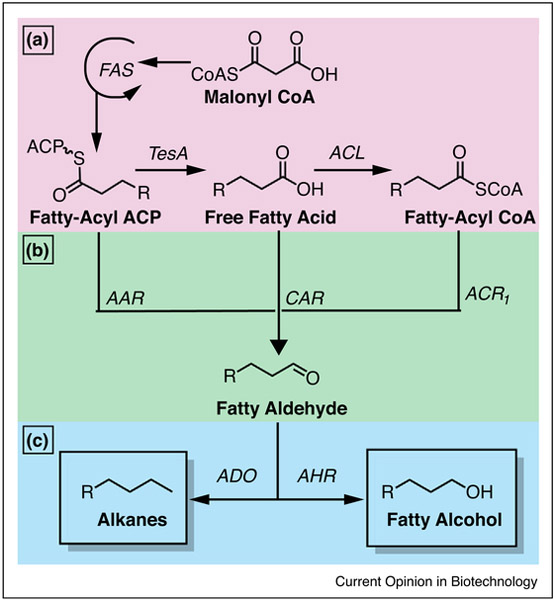
Figure 1.
Fatty acid synthesis of alkanes. (a) In the first step of fatty acid synthesis, acetyl-CoA and malonyl-CoA are transthioesterified to the fatty acid synthase (FAS), and the final product of each round of elongation is a fatty-acyl ACP. A thioesterase (TesA) can cleave the fatty-acyl ACP to generate a free fatty acid that reacts with an acyl-CoA ligase (ACL) to generate fatty-acyl CoA. (b) Fatty aldehydes can be generated from fatty-acyl ACP, free fatty acids, and fatty-acyl CoA through acyl carrier protein reductase (AAR), carboxylic acid reductase (CAR), and acyl CoA reductase (ACR1), respectively. (c) Fatty aldehydes can generate alkanes through aldehyde decarbonylase (ADO) and fatty alcohols through aldehyde reductase (AHR).