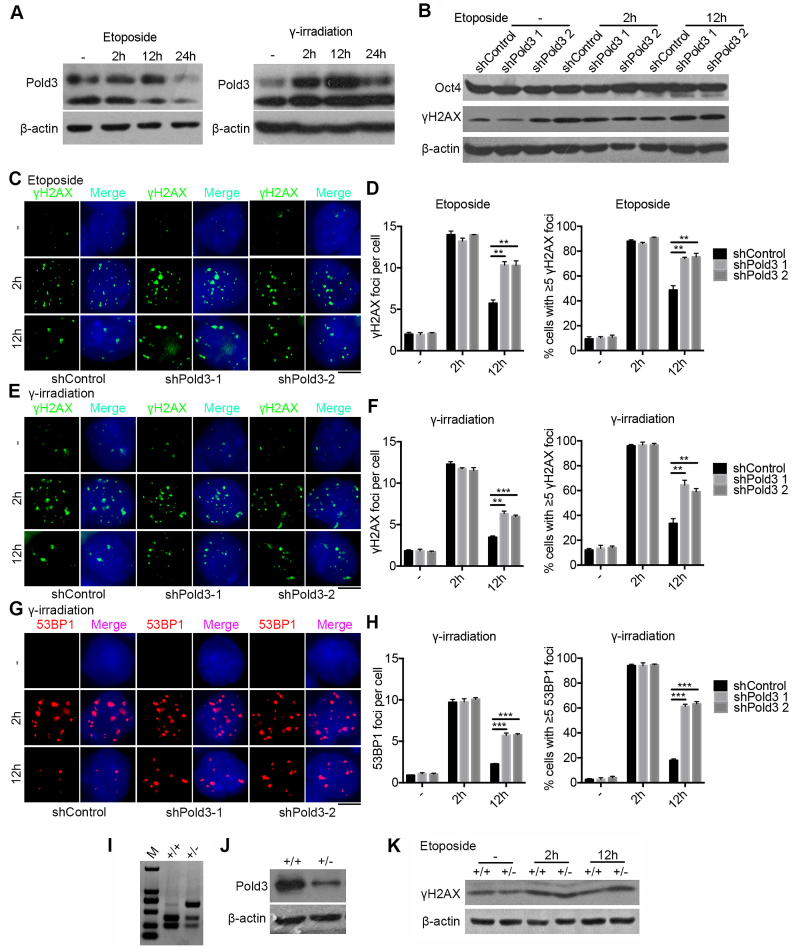
Figure 5.
Reduction of Pold3 impairs DNA repair in mouse ESCs. (A) Pold3 protein level increased following DSB induced by etoposide (2.5 μM) for 2 h or γ-irradiation (5 Gy). ESCs without treatment (−), or with treatment 2, 12 and 24 h after exposure to etoposide or γ-irradiation were harvested for western blot analysis. (B) Pold3 KD ESCs (N33) by exposure to 2.5 μM etoposide for 2 h express γH2AX protein at higher levels after 12 h recovery by western blot, while the protein level of Oct4 is not changed, like controls. (C) Pold3 KD ESCs (N33) by exposure to 2.5 μM etoposide for 2 h exhibit much more γH2AX foci after 12 h recovery compared with control by immunofluorescence. Scale bar, 5 μm. (D) Quantitative results of (C). Fifty cells were randomly counted in two repeated experiments. (E) Pold3 KD ESCs by exposure to 5 Gy γ-irradiation show more γH2AX foci after 12 h recovery compared with control by immunofluorescence. Scale bar, 5 μm. (F) Quantitative results of (E). n = 50 cells counted. (G) Pold3 KD ESCs by exposure to 5 Gy γ-irradiation display more 53BP1 foci after 12 h recovery compared with control by immunofluorescence. (H) Quantitative results of (G). n = 50 cells counted. (I) Genotyping of WT and Pold3+/− ESCs. (J) Reduced expression of Pold3 was confirmed by western blot in Pold3+/− ESCs, compared to WT ESCs. (K) Western blot analysis showing higher γH2AX protein level in Pold3+/− ESCs compared to control 12 h after exposure to etoposide for 2 h. Data represent mean ± SEM. **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.