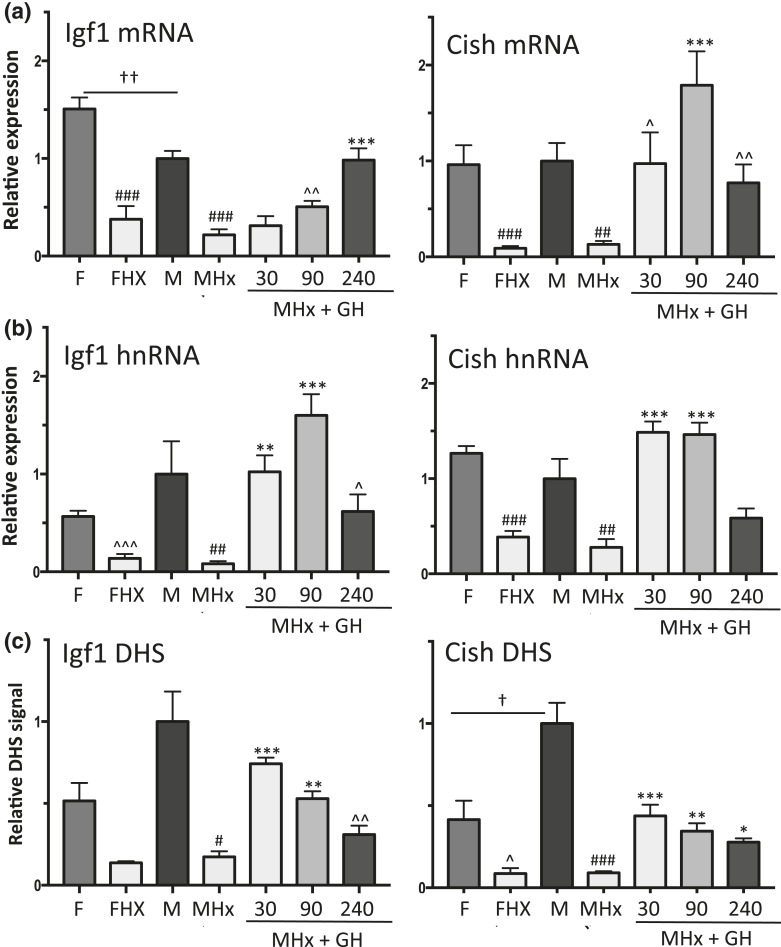
Figure 2.
Effects of a single GH pulse on chromatin accessibility and transcriptional response of sex-independent STAT5 target genes Igf1 and Cish. (a and b) RT-qPCR analysis of liver total RNA isolated from intact female (F) and male (M) mice, hypophysectomized female (FHx) and hypophysectomized male mice (MHx), and hypophysectomized male mice treated with a single pulse of GH and euthanized 30, 90, or 240 minutes later. qPCR was performed using primers that detect mature Igf1 and Cish RNA (a, mRNA) or primary unspliced RNA transcripts (b, hnRNA). RNA qPCR data were normalized to the 18S rRNA content of each liver RNA sample. (c) qPCR analysis of genomic DNA fragments released from DNase I–digested liver nuclei isolated from individual mice from the same treatment groups shown in (a) and (b). qPCR was carried out using primers that target open chromatin regions identified previously (51), which are marked DHS in Fig. 3(a) (Igf1) and Fig. 3(b) (Cish; also see Supplemental Table 1). DHS qPCR data were normalized to a DNase hypersensitive site at the Alb promoter [see Fig. 4(a)]. Data shown are mean ± SEM values based on n = 8 to 10 livers for each group (a and b) or n = 5 to 6 livers per group (c), except for the intact male group of (c), where n = 18 livers. Relative expression level and relative DHS activity of the intact male groups are set to 1. Significance values by ANOVA are indicated in each figure as follows: for intact male vs intact female, †P < 0.05, ††P < 0.01, †††P < 0.001; for hypophysectomized mice compared with intact mice of the same sex, #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01, ###P < 0.001; and for GH-treated vs untreated hypophysectomized mice, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. The symbol ^ indicates that statistical significance was reached only by t test and not ANOVA, at ^P < 0.05, ^^P < 0.01, and ^^^P < 0.001. Primers used for qPCR analysis are shown in Supplemental Table 1.