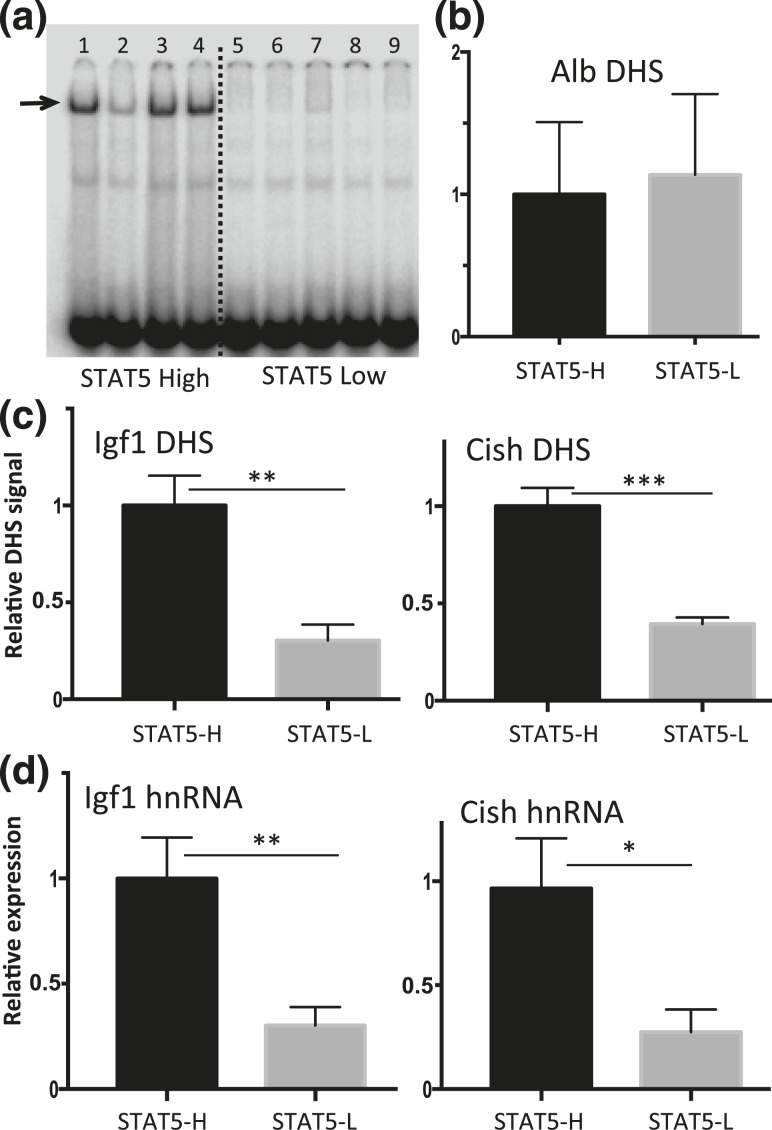
Figure 4.
Pulsatility of chromatin accessibility and STAT5-stimulated transcription in pituitary-intact male mouse liver. (a) EMSA analysis of whole liver extract using STAT5 EMSA probe. Individual intact male mouse livers show a binary pattern of liver STAT5-binding activity (STAT5-high, lanes 1, 3, and 4; STAT5-low, lanes 5 to 9; lane 2 shows a liver with STAT5-intermediate activity). Arrow indicates STAT5 activity band. (b and c) Isolated liver nuclei were digested with DNase I and the released DNA fragments were purified and assayed by qPCR for Alb, Igf1, and Cish DHS sites using primers shown in Supplemental Table 1. (b) Chromatin accessibility at the Alb promoter showed no significant difference between STAT5-high (STAT5-H) and STAT5-low (STAT5-L) livers and was used to normalize the DHS qPCR signal of the corresponding liver sample at all other DHS sites. (c) In contrast to the Alb DHS, chromatin accessibility was significantly greater in STAT5-high livers than in STAT5-low livers at the STAT5-bound DHS nearby Igf1 and Cish. (d) Transcription rates determined by RT-qPCR analysis of liver nuclear RNA using hnRNA primers specific to Igf1 and Cish were significantly higher in STAT5-high compared with STAT5-low livers. Data shown are mean values ± SEM for n = 9 livers per group (b and c) or n = 10 to 12 livers per group (d). The relative DHS activity and expression level of the STAT5-high groups are set to 1. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 by two-tailed t test.