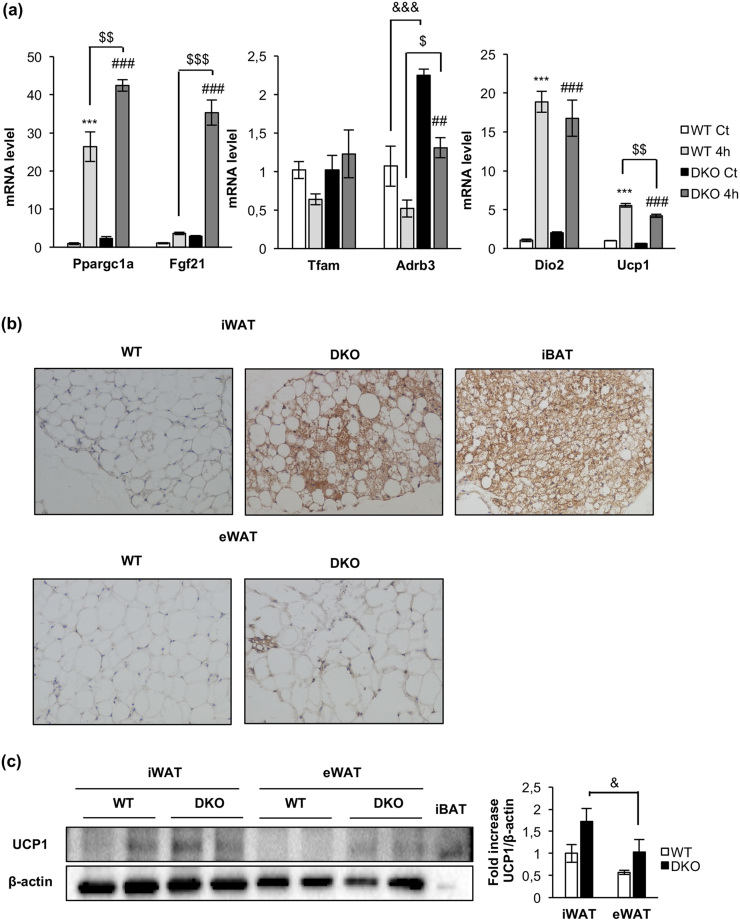
Figure 6.
Acute cold-induced gene expression and increased browning in inguinal fat depots in DKO mice. (a) Plot indicating fold-increased mRNA levels of iBAT genes from 12-month-old WT and DKO mice at thermoneutrality (WT, n = 3; DKO, n = 3) or after 4 hours (4h) of 4°C exposure (WT, n = 3; DKO n = 3). Results are presented as mean ± standard error of the mean. Statistical significance was assessed by one-way analysis of variance, followed by the Tukey test; ***P < 0.001 between WT control (Ct) and WT 4h groups; $P < 0.05, $$P < 0.01, and $$$P < 0.001 between WT 4h and DKO 4h; ##P < 0.01 and ###P < 0.001 between DKO Ct and DKO 4h; and &&&P < 0.001 between WT Ct and DKO Ct. (b) Immunohistochemistry for Ucp-1 protein (brown stain) in sections of inguinal WAT (iWAT) and epididymal WAT (eWAT) from 3-month-old WT (n = 3) and DKO (n = 3) mice. iBAT was used as a positive control. All images were taken at magnification of ×20. (c) Representative blots from UCP-1 protein expression in iWAT and eWAT (45 μg of protein was loaded) from 3-month-old WT (n = 4 animals per tissue) and DKO (n = 4 animals per tissue) and its corresponding quantitation. In this blot, 5 μg of iBAT was used as a positive control of UCP-1 protein expression. Results are presented as mean ± standard error of the mean. Statistical significance was assessed by one-way analysis of variance, followed by the Tukey test; &P < 0.05 between iWAT DKO and eWAT DKO groups.