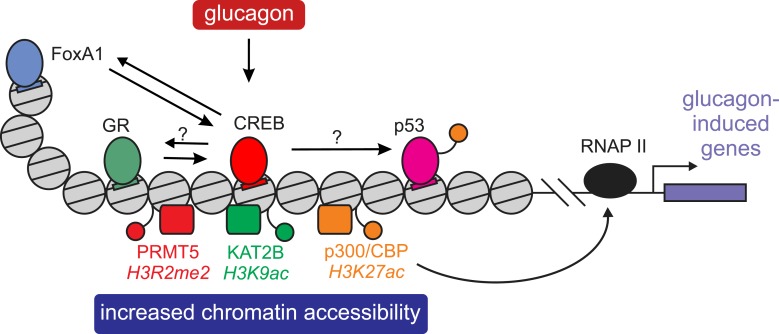
Figure 2.
CREB-mediated effects on chromatin and activation of companion TFs. Binding of the CREB/CRTC complex to chromatin initiates several events eventually promoting glucagon-dependent gene expression. CREB recruits histone-modifying enzymes (p300/CBP, KAT2B, and PRMT5) that increase the accessibility of chromatin to TF binding. Additionally, CREB-recruited p300/CBP promotes RNA polymerase II (RNAP II) activity and might activate other TFs by acetylation (e.g., p53). CREB also cooperates with other TFs via dynamic assisted loading, by which the binding of one TF facilitates binding of more TFs in the same enhancer via increased chromatin accessibility and enhancer activity. GR assists the loading of CREB onto chromatin, and so does FoxA1 (of note, CREB-FoxA1 cross talk was only described in prostate cells and not in the presence of glucagon). An assisted loading mechanism is often not unidirectional, and two TFs might enhance the binding of each other, as was shown in CREB-FoxA1 cross talk (and is also probable in the GR-CREB case).