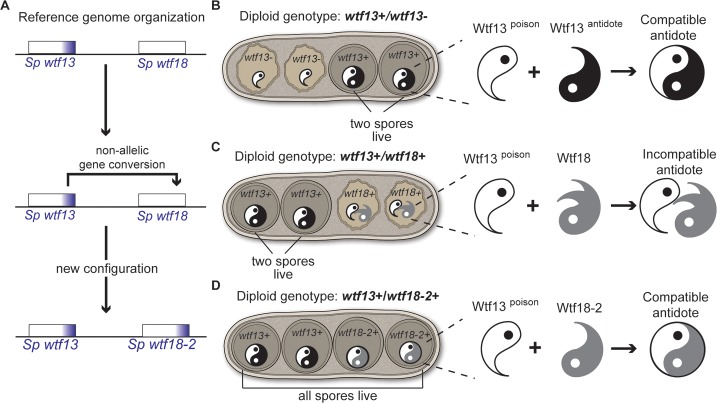
Fig 8. Model for wtf drive suppression.
(A) Sp wtf18-2 likely arose from a non-allelic gene conversion event between the Sp wtf18 allele present in the reference genome and Sp wtf13. This gene conversion event provided Sp wtf18 with the exon 6 present in Sp wtf13. The non-allelic conversion event happened from positions 1,580,047–1,580,343 to positions 1,806,929–1,807,206. This track includes part of wtf13 exon 5, intron 5, exon 6 and 3’ UTR region. (B) In wtf13 heterozygous diploids (wtf13+/ wtf13-), Sp Wtf13poison has the ability to kill every spore, but the Sp Wtf13antidote recognizes the Sp Wtf13poison protecting the spores that inherit the Sp wtf13+ allele. (C) In Sp wtf13+/ Sp wtf18+ diploids, the spores that inherit the wtf13+ allele are protected from the Wtf13poison by the Sp Wtf13antidote. The two spores that inherit the Sp wtf18+ allele die because Wtf18 does not neutralize the Sp Wtf13poison. (D) In Sp wtf13+/ Sp wtf18-2+ diploids, the spores that inherit the Sp wtf18-2+ allele are protected from the Wtf13poison because Sp Wtf18-2 makes an antidote capable of neutralizing the Sp Wtf13poison. Both Sp wtf13 and Sp wtf18 alleles are depicted at the same locus on opposite haplotypes, like the experiments in Fig 2A.