Figure 3.
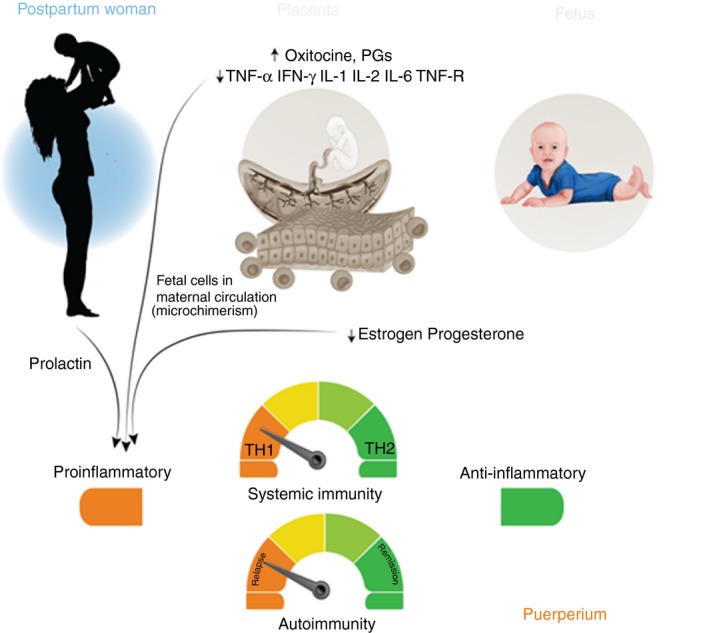
After childbirth, the protective influence of the placenta and the fetus is lost, and a pro‐inflammatory intrauterine environment prevails, determined mainly by maternal factors. A fall in the levels of estrogen, progesterone, glucocorticoids, and activated vitamin D is observed. Together these factors may condition an increase in the number of exacerbations observed during the postpartum period. PGs, Prostaglandins.
