Figure 3. Tak1 Interacts genetically with PGRP-LC.
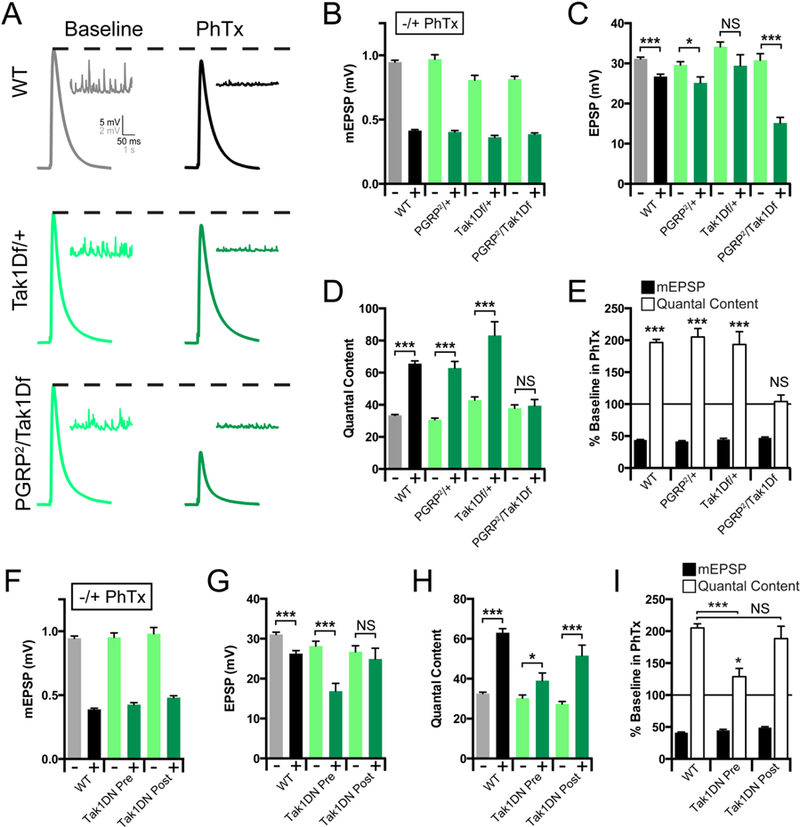
(A) Representative traces for EPSP (scale, 5 mV, 50 ms) and mEPSP (scale, 2 mV, 1 s) at baseline, and in the presence of PhTx, for the indicated genotypes. (B) Average mEPSP amplitude for each genotype in the absence (light bars) or presence (dark bars) of PhTx. (C) Average EPSP amplitude in the absence (light bars) or presence (dark bars) of PhTx. (D) Average quantal content in the absence (light bars) or presence (dark bars) of PhTx. (E) mEPSP amplitudes (filled bars) and quantal content (open bars) for each genotype in the presence of PhTx, normalized to baseline values in the absence of PhTx. (F) Average mEPSP amplitude for each genotype in the absence (light bars) or presence (dark bars) of PhTx. (G) Average EPSP amplitude in the absence (light bars) or presence (dark bars) of PhTx. (H) Average quantal content in the absence (light bars) or presence (dark bars) of PhTx. (I) mEPSP amplitudes (filled bars) and quantal content (open bars) for each genotype in the presence of PhTx, normalized to baseline values in the absence of PhTx. Data are presented as average (+/− SEM) and statistical significance determined by Student’s t-test (unpaired, two-tailed). See also Supplemental Figure 4.
