Figure 4. Irisin targets mitochondria-dependent oxidative stress pathway for cardioprotection.
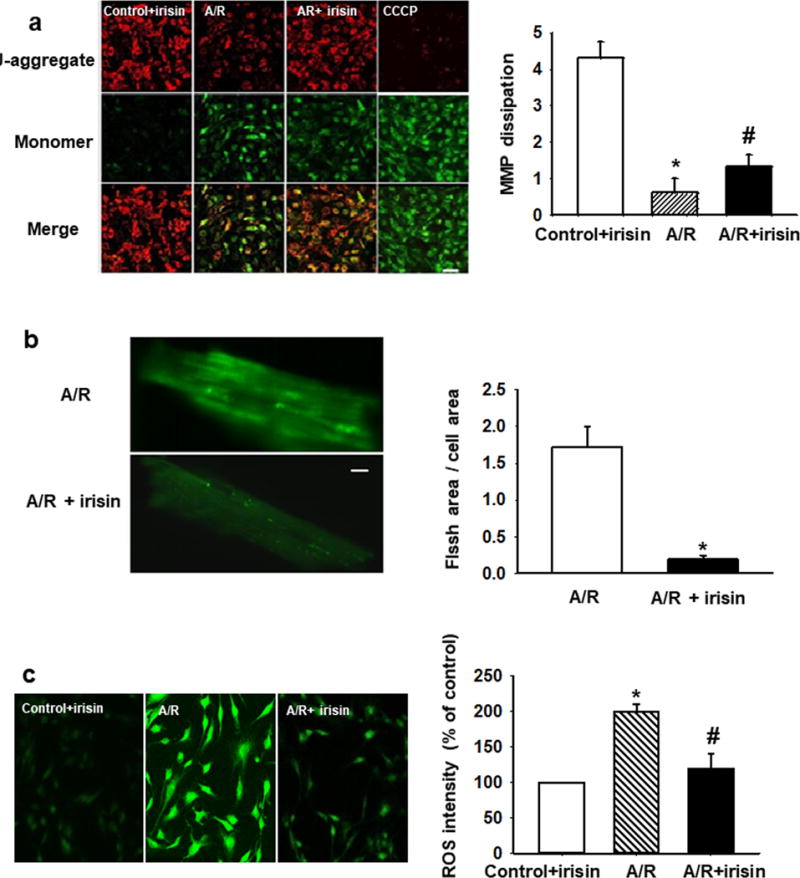
(a) Irisin treatment preserved MMP after A/R injury in H9c2 cells. Red fluorescence of JC-1 was reduced after A/R injury and could be partially rescued by irisin treatment (upper panels). Dissipation of MMP as determined by enhancement of green monomeric form of JC-1 could be partially rescued by irisin (middle panels). A mitochondrial uncoupling agent, CCCP (10mM), was used to completely dissipate the MMP. MMP was quantified as the ratio of red and green fluorescence of JC-1. Irisin treatment rescued A/R induced MMP dissipation. (n=4, *P<0.01 vs. control+irisin, #P<0.05 vs. A/R, Bar = 80 μm). (b) Mitochondria superoxide FLASH events from mouse cardiomyocytes subjected to A/R (upper panel), and with incubation of 100 ng/ml irisin in the extracellular solution (lower panel). Summation of 100 continuously recorded images of cpYFP was presented. Myocytes incubated with irisin show reduced FLASH signals. See supplementary movies for the dynamic changes in FLASH events. Quantitative analysis of mitochondrial FLASH events. n= 9-10 cells/group from 4 mice (*P<0.05 vs. A/R, Bar = 10 μm). (c) Total ROS production in H9c2 cells was quantified by DHE staining. Irisin treatment reduces A/R induced ROS (n=10, *P<0.01 vs. control+irisin, #P<0.05 vs. A/R, Bar = 80 μm).
