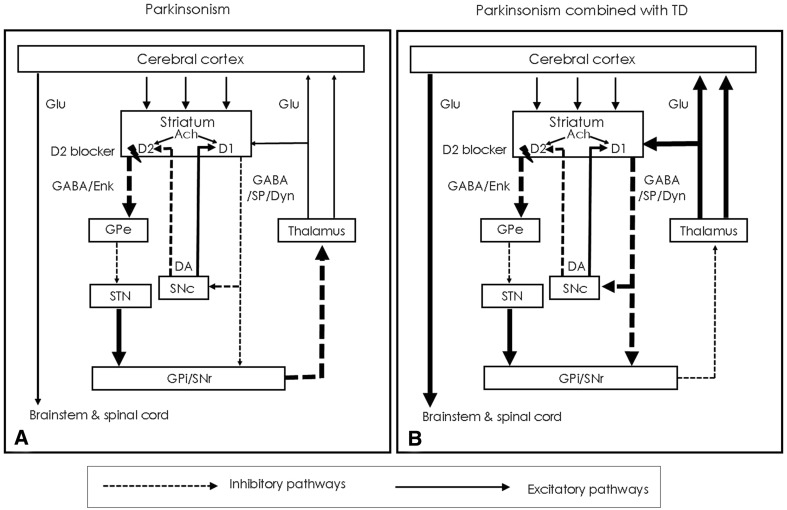
Fig. 1.
Changes in basal ganglia-thalamocortical motor loop due to blockade of D2 receptors by DRBAs. The blockage of D2 receptors by DRBAs in the striatum leads to disinhibition of GABA- and encephalin-containing striatal neurons at the origin of the indirect pathway, followed by a disinhibition of the subthalamic nucleus. This leads to increased GABAergic inhibition of the thalamocortical projection by facilitation of the inhibitory projection from the GPi/SNr (a). Chronic D2 receptor blockade also induces changes in the direct pathways of the basal ganglia-motor loop to cause orolingual dyskinesia (b). DA dopamine, DRBAs dopamine receptor blocking agents, GABA gamma-aminobutyric acid, GPe globus pallidus pars externa, GPi globus pallidus pars internal, SNc substantia nigra pars compacta, SNr substantia nigra pars reticulata, STN subthalamic nucleus, TD tardive dyskinesia.
Reproduced as per the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0) from [2])