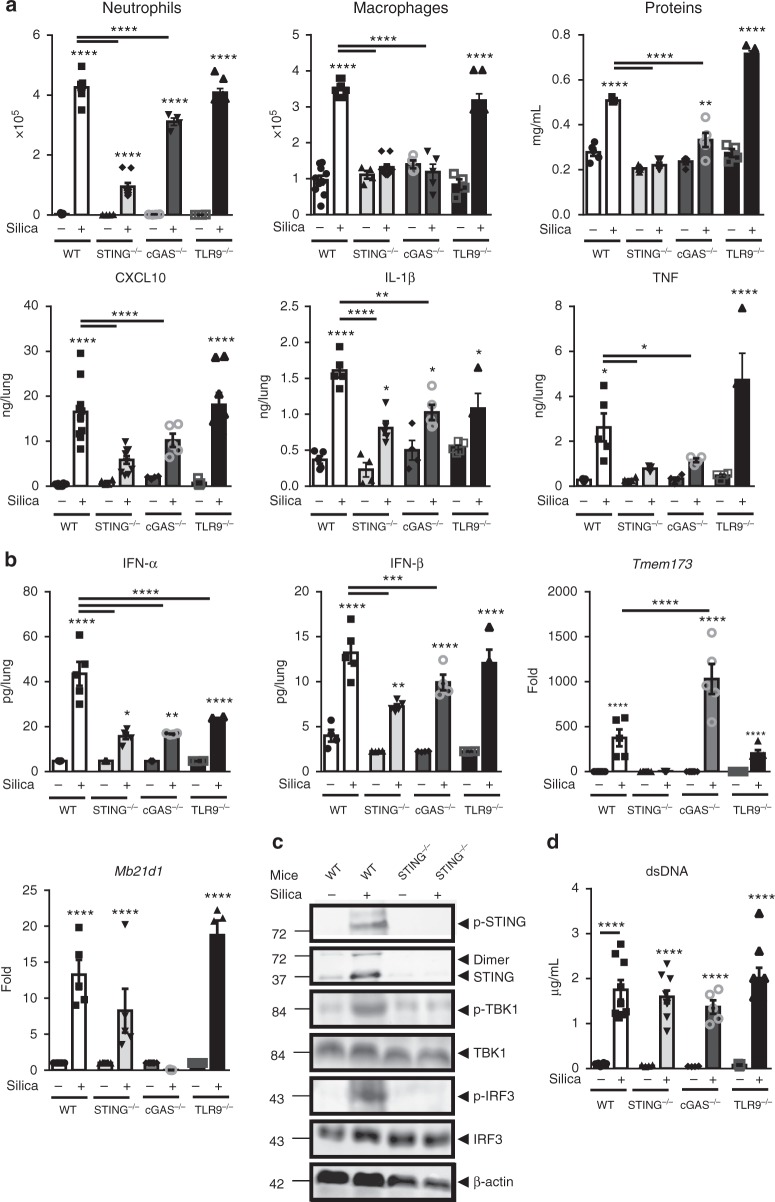
Fig. 3.
DNA sensors STING and cGAS are essential, while TLR9 is dispensable, for silica-induced lung inflammation. Silica microparticles (1 mg/mouse, i.t.) or saline vehicle were administered in WT, STING−/−, cGAS−/−, and TLR9−/− mice and the different parameters were analyzed on day 7. a Neutrophils, macrophages, and protein extravasation were measured in the BALF and the lung levels of CXCL10, IL-1β, and TNF were determined by ELISA. b Pulmonary IFN-α and IFN-β protein concentrations determined by multiplex immunoassay, and Tmem173 and Mb21d1 transcripts measured by real-time PCR. c Immunoblots of STING/IRF3 axis in the lung of WT and STING−/− mice, including phospho-STING, STING, phospho-TBK1, TBK1, phospho-IRF3, and IRF3, with β-actin as a reference. d Concentration of extracellular dsDNA in the acellular BALF fraction. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ****p < 0.0001 (Kruskal–Wallis test followed by Dunn post test). Data are presented as mean ± SEM and are representative of three (a, b, d) and two (c) independent experiments. (a, b, d): mice per group: n = 10 (WT NaCl), n = 8 (WT silica), n = 4 (STING−/− NaCl), n = 7 (STING−/− silica), n = 4 (cGAS−/− NaCl), n = 5 (cGAS−/− silica), n = 5 (TLR9−/− NaCl), n = 6 (TLR9−/− silica). Immunoblots are representative of n = 6 samples from two independent experiments (c). Each symbol represents an individual mouse. Source data are provided as a Source data file