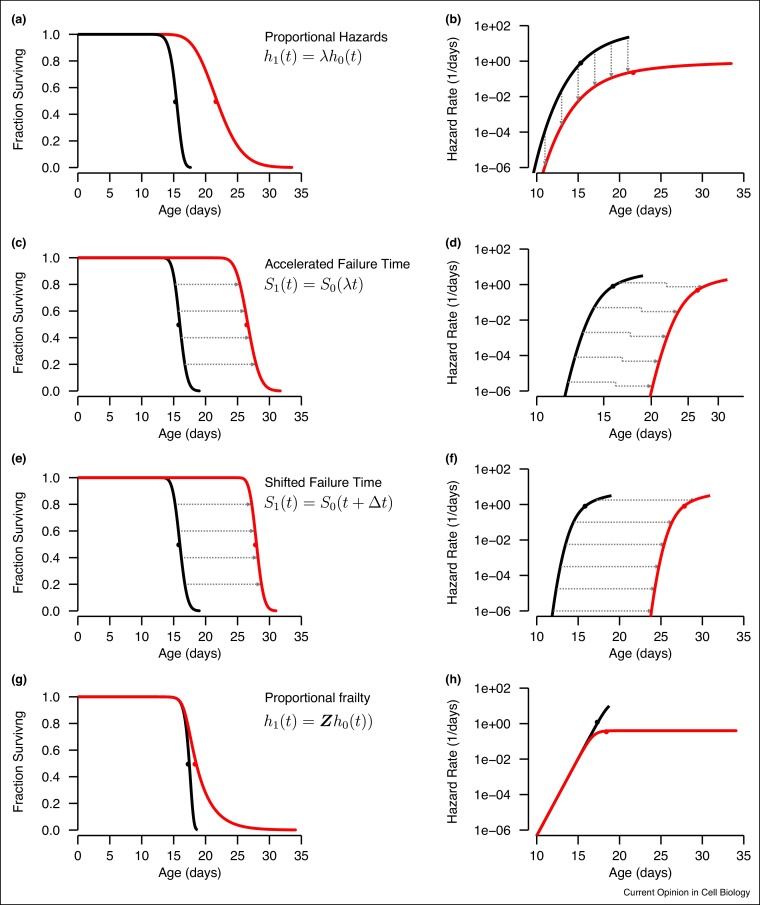
Figure 3.
Semi-parametric models of lifespan data. Semi-parametric models describe differences between populations in a way that does not depend on any particular parametric form of the survival curve of hazard function. (a,b) Proportional hazards functions assume that two populations’ hazard functions are offset by a constant ratio. (c,d) Accelerated Failure time models assume that two populations’ survival curves are related by a temporal scaling, corresponding to simultaneous shift of the hazard functions, up and to the right such that h1(t) = λh0(λt). (e,f) Accelerated Failure time models are easily modified to model populations whose survival distributions are shifted (rather than scaled) in respect to time. (g,h) The existence of heterogeneity within a population in respect to the risk of death produces a deceleration, or leveling-off of the hazard function and a corresponding long-tail of the survival function.